Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1000
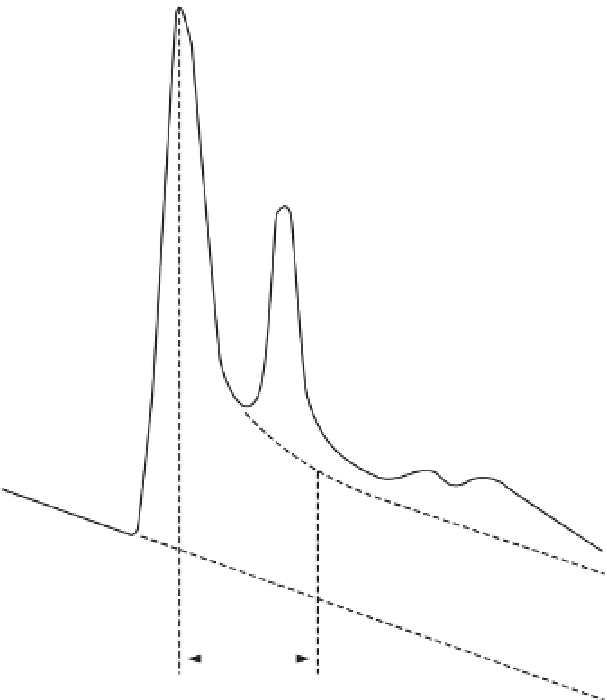
Figure 4.11
Procedure for
using the recession-curve
displacement method to
estimate groundwater recharge
in response to a recharge event
(after Bevans,
1986
; Rutledge,
1998
): (1) Compute recession
index,
K
RI
(32 d/log cycle); (2)
Compute critical time,
T
c
(0.2144
K
RI
or 6.86 d); (3) Locate time
6.86 d after peak; (4) Extrapolate
pre-event recession to
Q
bf
1
(0.5 m
3
/s); (5) Extrapolate post-
event recession to
Q
bf
2
(2.3 m
3
/s);
(6) Compute total recharge,
2 × (1.8 m
3
/s) × 32 d/2.3026 ×
86 400 s/1 d = 4.32 × 10
6
m
3
.
Recharge
event of
interest
Daily streamflow
Extrapolated
groundwater
discharge
100
10
Q
bf
2.3 m
3
/s
2
1
Q
bf
0.5 m
3
/s
1
6.86 d
Tc
0.1
1
10
20
31
Days
Equation (
4.12
) estimates the amount of water,
from any instantaneous recharge event, that
remains stored in the subsurface at any time. On
this basis, Meyboom (
1961
), Rutledge and Daniel
(
1994
), and Rutledge (
1998
) claimed that the
recession-curve displacement method provides
an estimate of recharge, as opposed to base flow
(i.e. terms in Equation (
4.1
), such as evapotrans-
piration of groundwater and interaquifer flow
are included in the estimates generated by the
method). Results of recession-curve displace-
ment analyses are often reported as recharge.
Yet loss of groundwater to evapotranspiration
or interaquifer flow violates the underlying
assumptions of the method. A tacit assump-
tion in the Rorabaugh approach is that all of
the water that arrives at the water table from a
recharge event eventually drains to the stream.
Rutledge (
2000
) considered two hypothetical
scenarios with the same total recharge. In the
first case, all recharge discharges to the stream;
in the second, some water is diverted to evapo-
transpiration. The streamflow recession curves
for these two cases differed, as did the esti-
mates of recharge according to Equation (
4.13
).
Rutledge (
2000
) concluded that the method was
estimating net recharge (total recharge minus
groundwater evapotranspiration). Nonetheless,
several studies (Rutledge and Mesko,
1996
;
Mau and Winter,
1997
; Arnold and Allen,
1999
;
Chen and Lee,
2003
; Risser
et al
.,
2005a
) found
that the recession-curve displacement method
produced estimates that were consistently
greater than those from other hydrograph