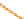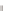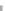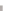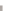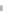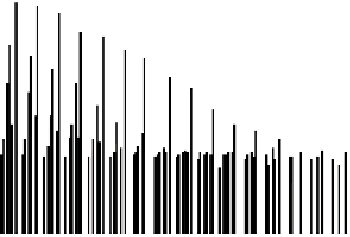Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
0.08
Scene 1
Scene 2
Scene 3
Scene 4
Scene 5
Scene 6
0.07
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.01
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
24
25
Batch Index
Figure 4.8.
Solving time for a batch created by global batching.
demand for more memory operations. We can guess that the increase saturates
the memory system at the point at which solver time exceeds the constant time.
We can also see solving time starts increasing when more than 2,000 constraint
pairs are scheduled in a batch. As the number of constraints increases further,
performance gradually decreases.
From Figure 4.8, we can get a lower bound of a batch's solving time as 0.021
ms. Multiplying the minimum time required to solve a batch by the number of
batches for each benchmark scene, we can estimate the lower bound of the time
required for the two-level constraint solver plotted in Figure 4.7. However, we
can see that the measured solving time using the two-level constraint solver is
800
Scene 1
700
Scene 2
600
Scene 3
500
Scene 4
400
Scene 5
300
Scene 6
200
100
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
24
25
Batch Index
Figure 4.9.
The number of constraint pairs in each batch when global batching is used.