Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
•
neighbours sharing only a corner
= average of costs in the neighbouring cells
multiplied by 1.4142 (e.g.
(45 + 42)
/
2
=
87
/
2
= 43.5 ¥ 1.1412 = 61.5).
h e cost surface procedure (note the connections with Section 6.5) can be outlined
as follows:
•
Compute the cost distances from each source cell to its neighbours.
•
Select the smallest cost distance and compute the smallest cost distance to that
cell's neighbours—these cells are activated.
h e next activated cell with the smallest accumulative cost distance is selected.
•
Next, compute the smallest cost distance to that cell's neighbours. Every time a
cell becomes accessible to a source cell through a dif erent path it is reactivated
and its accumulative cost must be recalculated because the new path may have
a smaller accumulative cost (Chang, 2008). If it does not, then the accumulative
cost value remains the same.
Continue this process until all smallest accumulative cost distances have been
•
computed.
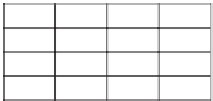
45
44
44
43
1
43
42
39
36
38
32
34
35
39
41
37
38
2
Cost grid
Source cells
Figure 10.12
Cost grid and source cells.
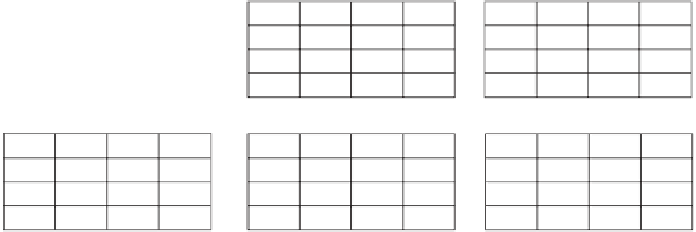
0
44
44.5
61.5
44.5
44.5
61.5
83.9
0
0
44
61.5
87.4
72
44
87.4
72
50.9
36.5
50.9
36.5
50.9
36.5
37.5
0
0
37.5
76.5
37.5
0
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
0
44.5
88.5
0
44.5
88.5
111.5
0
44.5
61.5
44
84.5
87.4
72
44
61.5
87.4
72
44
61.5
87.4
72
84.5
83.9
50.9
36.5
84.5
83.9
50.9
36.5
83.9
76.5
50.9
37.5
36.5
0
76.5
37.5
0
76.5
37.5
0
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
0
44.5
88.5
111.5
44
61.5
87.4
72
84.5
116.5
83.9
50.9
36.5
37.5
0
76.5
Step 7: Least accumulative
cost distances
Figure 10.13
Cost surface derivation.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search