Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
18.3.3 Confirmation of Dystroglycan Knockdown
by qRT-PCR Analysis
To further confirm that siRNA injection specifically knocked down dystroglycan
gene expression, we also performed real-time qRT-PCR. Briefly, total RNA was
isolated from uninjected control, KD control, andMD zebrafish at 4, 6, and 20 hpi and
qRT-PCR was performed using conventional methods. Results showed that dystro-
glycan gene expression (expressed as percent of uninjected control) decreased in MD
zebrafish at 4, 6, and 20 hpi (85.1
3.2%, respec-
tively), confirming dystroglycan knockdown and results by immunostaining
(Fig. 18.3).
8.0%, 94.2
8.4%, and 59.5
18.3.4 MD Zebrafish Exhibit Short, Disorganized
Myotomes
MD zebrafish exhibited short myotomes lacking the characteristic chevron, V-shaped
structure (Fig. 18.2, red arrow; thick black outline) (Parsons et al., 2002). In contrast,
KD control zebrafish exhibited normal V-shaped myotomes (Fig. 18.2, black arrow;
thick black outline). In MD zebrafish, some myotomes were disrupted or missing.
Myotomes in the tail are primarily comprised of muscle fibers that align along the
anterior-posterior axis of the body and tail length reflects muscle fiber length.
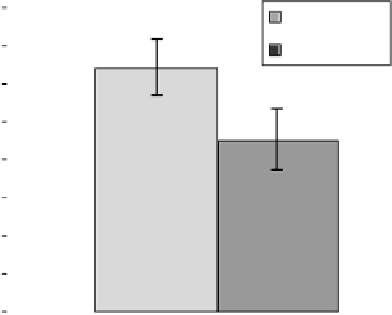
Next, we measured eight myotomes along the anterior-posterior body axis (two
anterior and six posterior to the anal pore) (blue lines, Fig. 18.2). A significant
difference was observed (
P
¼7.110
14
); mean length for KD control zebrafish was
0.642
0.075 mm and for MD zebrafish was 0.450
0.079mm (
n
¼
33), which was
30% shorter ((1
0.450/0.642)
100%
¼
29.9%) than KD control (Fig. 18.4).
0.800
KD controls
MD
0.700
0.600
0.500
0.400
0.300
0.200
0.100
0.000
Figure 18.4
Decreased myotome length in MD zebrafish. Myotomes (eight myotomes) in
3dpf MD zebrafish were 39% shorter than KD control (
P
10
14
,
n
¼
7.1
¼
33).


Search WWH ::

Custom Search