Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
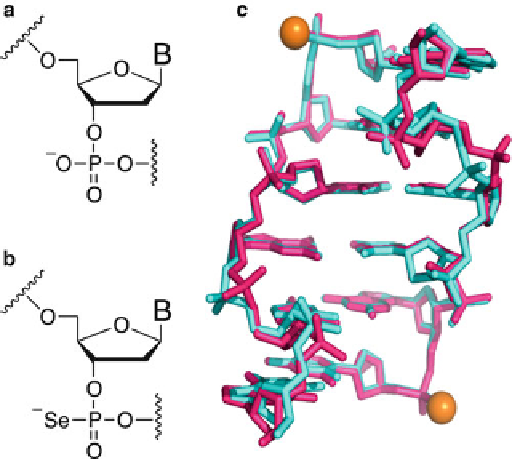
Fig. 3.4
Structure
comparison
of
native
and
phosphoroselenoate-linked
DNAs.
(
a
)
Native
phosphate.
(
b
)
Phosphoroselenoate.
(
c
)
Superimposed
comparison
of
PSe-ZDNA
(5
0
-C
p-Se
GCGCG-3
0
)
2
,
A
cyan
,
PDB
ID:
1VRO,
1.1
resolution
and
native-ZDNA
(5
0
-CGCGCG-3
0
)
2
,
pink
, PDB ID: 2DCG, 0.9
A resolution. Selenium atoms are labeled as
orange
ii
selenide) [
54
], the organometallic reagent (iPrC
(5)
H
(4)
)
(2)
TiSe
(5)
[
55
], and Se-
(2-cyanoethyl)phthalimide [
56
]. These selenium transfer reagents offer highly
efficient conversion; however, the newly generated P-chiral center leads to a
mixture of two diastereoisomers, if one PSe group is introduced. If multiple PSe
groups are introduced, 2n diastereoisomers will be generated, which makes the
diastereoisomeric separation impossible. Since the separation of stereoisomers is
quite time-consuming, in 2005, Stec and coworkers successfully developed a new
strategy based on oxathiaphospholane approach, which allows diastereoisomerically
pure phosphoroselenoate DNA synthesis [
57
].
3.3.2
Enzymatic Synthesis of Phosphoroselenoate Nucleic
Acids
Although numerous Se-transferring methods have been developed, synthesizing
3
0
-end modified or longer PSe-oligonucleotides with multiple PSe groups remains
challenging, due to deselenization during solid-phase synthesis or purification
challenges. Thus, we have developed the enzymatic approaches for both PSe-
Search WWH ::

Custom Search