Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
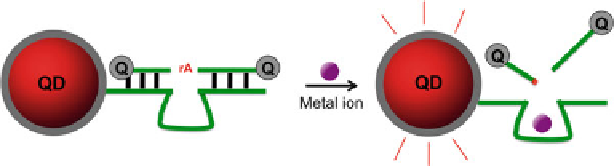
Fig. 13.8
FRET sensor of metal ions based on DNAzyme conjugated QDs. The ZnS-capped CdSe
QD is coated with a thin silica shell for covalent modification of the DNAzymes. The target metal
ion-induced cleavage of the DNAzyme substrate can recover the fluorescence from the QD
at 525 nm. Similarly, cocaine sensors were also constructed by using QDs Q2
with emission at 585 nm. As these two sensors can be carried out under the same
conditions, this design allowed the detection of both analytes in one pot. While two
emission peaks at 525 and 585 nm from the sensor composed of a mixture of both
assemblies were initially quenched, the fluorescence signal was increased at 525 nm
with the addition of 1 mM adenosine or at 585 nm in the presence of 1 mM cocaine.
Addition of both analytes resulted in fluorescence increase at both 525 and 585 nm.
This result proved the high selectivity of both systems, which can be applied to the
detection of more analytes simultaneously.
By combining the QDs with high ion-specific DNAzymes, Fan and coworkers
developed highly sensitive and specific heavy metal sensors (Fig.
13.8
)[
113
]. The
DNAzymes were attached onto the surface of carboxyl-silanized QDs, in which
dual quenchers were labeled on both substrate and DNAzyme segments to quench
fluorescence of the QDs based on FRET. In the presence of metal ions, the emission
was enhanced due to the cleavage of DNAzymes. The detection limit of 0.2 and
0.5 nM was achieved for Pb
2C
and Cu
2C
, respectively, which is a 50- and 70-
fold respective improvement over the reported sensors from organic dye molecules.
Multiplexed detection for Pb
2C
and Cu
2C
was also demonstrated using two different
types of QDs.
13.3.2
Lanthanide Ion Doped Upconversion Nanoparticles
Based Fluorescent Sensor
The development of luminescent nanoparticles for biosensing and bioimaging has
received greater attention in recent years. However, most of these nanoparticles use
short-wavelength (UV or blue) photon excitation. Most recently, lanthanide ion-
doped upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), typically NaMF
4
:Yb
3C
/Ln
3C
(M
D
Y
or Gd, Ln
D
Er or Tm), appeared as an exciting new type of nanophosphors for
biomedical applications [
114
-
122
]. UCNPs show shorter wavelength luminescence
from the deep-UV to the NIR upon being photoexcited by the NIR light (typically
around 980 nm) where the auto-absorption of biomolecules is quite weak, resulting
Search WWH ::

Custom Search