Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
O
Na
+
O
-
O
S
Palmitic Acid Methyl Ester Sulfonate (MES)
O
O
O
O
O
O
OH
S
N
+
-
O
O
O
Di-Dodecyl Esterquat
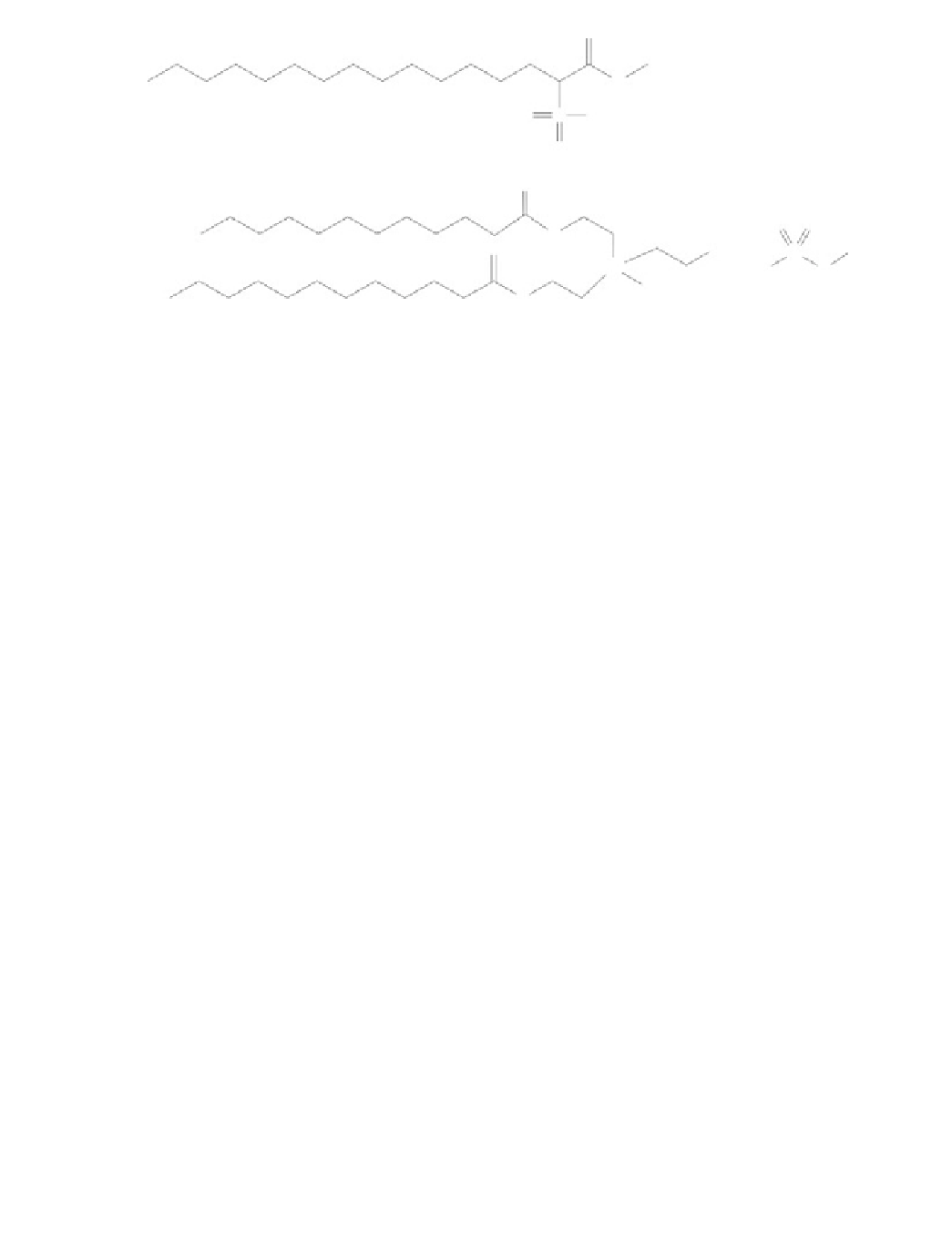
Figure 10.2
Molecular structure of industrial bio-based surfactants that are typically synthesized
chemically.
Holstebro, Denmark) and “All/Surf” from Unilever, and are produced by Lion (Johore,
Malaysia), Cognis (Selenagor, Malaysia), Stepan (Northfield, IL; 50 000 tonnes/year) and
Huish Detergents (Salt Lake City, UT; 80 000 tonnes/year), among others (Roberts
et al
.,
2008 ; McCoy, 2008 ; Hayes, 2009 ). Esterquats, cationic, quaternary ammonium, surfactants
derived from FAME (Figure 10.2), are important biodegradable rinse-added fabric softeners
and ingredients of hair conditioners, dyes, and bacterial and sanitizer products, including
swimming pool biocides, produced by Undessa (Barcelona, Spain) among others (Hayes,
2009 ; Mishra and Tyagi, 2007 ; Overkempe
et al
., 2003). A novel bio-based surfactant series
has also been reported, where bio-based hydroxylated diacids, malic and tartaric acids, are
covalently attached to fatty acid chlorides under solvent-free conditions to produce fatty
acyl-conjugated anhydrides, then covalently attached to triethylene glycol to produce
Gemini surfactants that are biodegradable and perform outstandingly as surfactants
(Altenbach
et al
., 2010 ).
The examples given above are bio-based surfactants that are currently and most probably
in the future will be produced chemically. There are several commercial surfactants that can
be potentially produced, or partially produced,
via
bioprocessing, particularly fatty acid-
polyhydric alcohol (or polyol) esters and fatty alcohol-polyol ethers, employed in foods,
cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals (Figure 10.3). Alkyl polyglycosides, or APGs (e.g.,
β
-C
12
G
2
; Figure 10.3), have numerous applications in pharmaceuticals
and cosmetics due to their high biocompatibility, and are manufactured worldwide, with a
capacity of nearly 85 000 tonnes per year (e.g., Glucopon
®
, Plantacare
®
, and Plantaren
®
product lines from Cognis, Cincinnati, OH) (Savic
et al
., 2010 ; Hill, 2009 ). Saccharide-
fatty acid esters are useful emulsifiers in foods, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals which also
possesses antimicrobial activity (Otomo, 2009).
Sorbitan esters (known as Span
®
) and their derivatives containing poly(ethylene glycol),
that is, poly(ethylene oxide), or equivalently, “ethoxylate” groups (known as Tween
®
;
Figure 10.3), also known collectively as polysorbates, have numerous uses. These three
surfactants can be tailored to possess a specific hydrophilic-lipophilic balance, to direct
their employment for oil-in-water (greater hydrophilicity) or water-in-oil (greater
lipophilicity) type emulsification, through adjusting the fatty acyl or alcohol tail length and
degree of unsaturation, the chemical structure and degree of polymerization of the polyol
-dodecyl maltoside,
β



Search WWH ::

Custom Search