Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
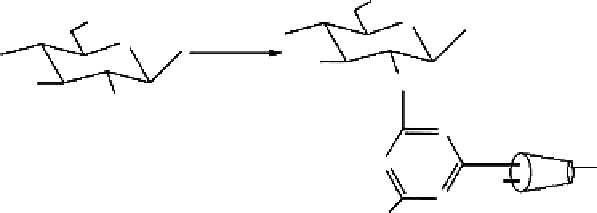
2.10.2 grafting of CD onto Chitosan by Nucleophilic Substitution
Monochlorotriazinyl groups are often encountered in textile chemistry, where they are
used as functional groups of reactive dyes for the finishing of wool and cellulose. Their
reactivity is based on the ready nucleophilic displacement of the chlorine atom by the
amino or hydroxyl groups carried by the polymer that builds the fiber. Martel et al. [218]
used a monochlorotriazinyl derivative of β-CD as a reagent for the grafting of β-CD onto
chitosan. In this approach, as shown in
Figure 2.26,
β-CD was coupled to chitosan by the
intermediate of its monochlorotriazinyl derivative through the nucleophilic substitution of
the chloride atom by the amino groups. The resulting products were not soluble, but did
swell, in water, nor were they soluble in the numerous organic solvents. Because the aver-
age DS of the monochlorotriazinyl derivative of β-CD was 2.8, the reaction yielded cross-
linked insoluble products due to both intra- and intermolecular bondings occurring with
the polymer chains.
2.10.3 grafting of CD onto Chitosan by using Tosylated
β
-CD
Chen and Wang [219] synthesized β-CD-graft-2-chitosan by reacting β-CD with
p
-toluene-
sulfonyl chloride and then grafting with chitosan. The reaction scheme for the synthesis is
shown in
Figure 2.27.
The products obtained by this method were soluble in water, metha-
nol, DMSO, and DMF. The polymer inclusion complex of β-CD-graft-2-chitosan with iodine
was prepared and its inclusion ability was studied. The experimental results showed that
a substantial amount of iodine was included with β-CD-graft-2-chitosan and formed a
stable inclusion complex, while chitosan alone had little ability to absorb iodine. The stron-
ger inclusion ability of β-CD-graft-2-chitosan with iodine was caused by the special hydro-
phobic cavity structure of β-CD-graft-2-chitosan. The absorption of iodine was considered
to be caused by
n-
δ charge transfer between amino groups of chitosan and iodine mole-
cules [220].
2.10.4 grafting of CD onto Chitosan by using 1,6-Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
6-Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HMDI) is generally utilized as a strong cross-linker of amino
or hydroxyl groups because it possesses two isocyanate groups (-N=C=O). Under suitable
conditions (pH < 6), the hydroxyl groups of chitosan react with an isocyanate to form a
OH
Monochlorotriazinyl
derivative of CD
OH
O
O
OH
DMF, 60°C
NH
OH
NH
2
N
N
CH
2
OH
CD
HO
N
NaO
Figure 2.26
Reaction scheme for the synthesis of β-CD-graft-chitosan by the nucleophilic substitution reaction. (From
Martel, B. et al. 2001.
J Polym Sci A-Polym Chem
39: 169-176. With permission.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search