Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
250
200 nm
200
103
150
83
60
100
50
0
0
1
2 3 4
Solution concentration (wt.-%)
5
6
7
8
9
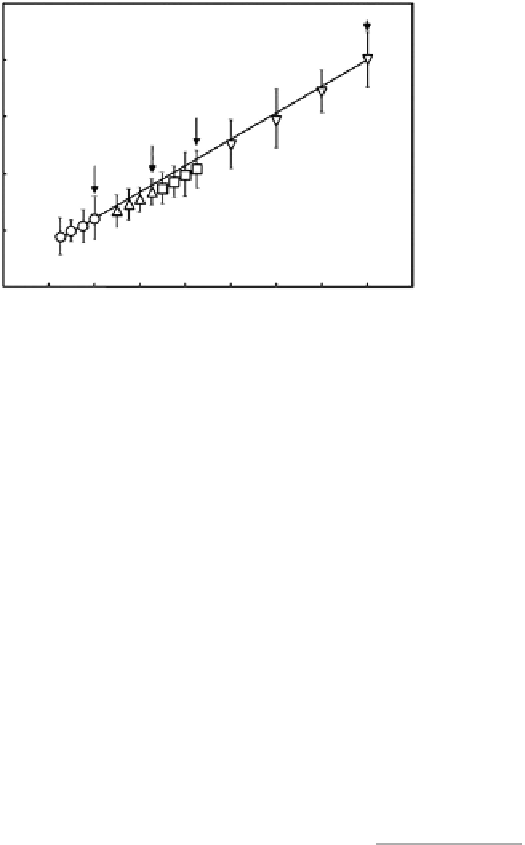
Figure 9.5
Relationship between the concentrations of the prespun chitosan/TFA solutions and the mean diameters of the
electrospun chitosan fibers. Numbers with arrows indicate the mean fiber diameter in the optimized spinning
condition, giving the relatively homogeneous fiber networks. (From Ohkawa, K. et al. 2006.
Biomacromolecules
7:3291-3294. With permission.)
9.2.3 Chitosan-based Microsphere Scaffolds
Recently, microspheres have also been assessed as scaffolds for tissue engineering, and
new strategies, such as sintering and fusion methods, have been investigated to obtain
suitable scaffolds that mimic the tissue environment for cells. Most of the concepts based
on the use of such scaffolds require the implantation kind of the hybrid constructs through
a surgical procedure. The process of scaffold fabrication consisted of the following steps.
(1) Preparation of chitosan-based microspheres: polymer dissolving, spheres production
by extrusion of the solution to the precipitating bath, pH neutralization, scaffold forma-
tion, chitosan cross-linking, rinsing, and drying. (2) Microsphere scaffold formation:
TAble 9.1
Electrospun Chitosan Composites Nanofibers
Average Fiber
Diameter (nm)
Composites
Solvent
References
Chitosan/collagen
HFP/TFA
415-810 (−)
[21,22]
Chitosan/gelatin
TFA/DCM
100-220
[23]
Chitosan/agarose
TFA/DCM
140-1500 (+)
[24]
Chitosan/PEO
aq. AA
80-180
[25]
Chitosan/PLA
TFA
[26]
40-1200 (−)
Chitosan/PCL
Formic acid/acetone
112.9-139.6
[27]
Chitosan/PVA
aq. AA
20-100
[28]
Chitosan/PLGA
Chloroform/DMF
272
[29]
Note:
(+), diameter of composites increases with increasing chitosan content; (−), diameter
of composites decreases with increasing chitosan content.
HFP, 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropanol; TFA, trifluoroacetic acid; DMF, N,N-dimethyl-
formamide; aq. AA, aqueous acetic acid solution; DCM, dichloromethane; PVA, poly(vinyl
alcohol); PEO, poly(ethylene oxide); PLA, poly(lactic acid); PLGA, poly(lactide-co-glycolide);
PCL, polycaprolactone.



Search WWH ::

Custom Search