Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
scaffolds were fabricated by packing and agglomeration of the microspheres. On the one
hand, chitosan-based microspheres can be packed with the use of a solvent. The acidic
solvent dissolves the external surfaces of the spheres so that they get stuck together and
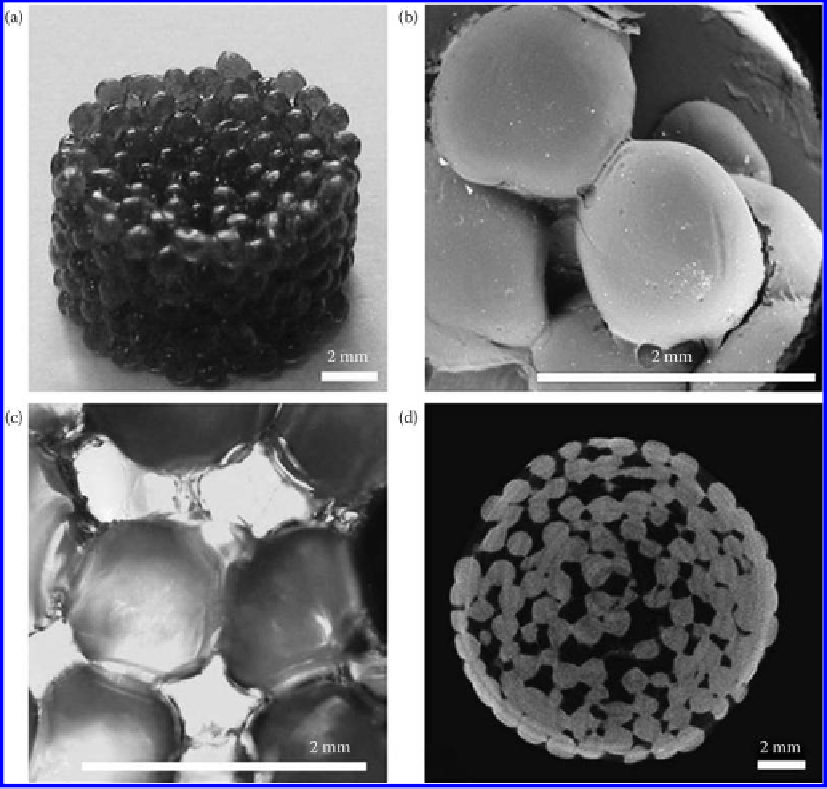
their structure becomes tight and durable. As shown in Figure 9.6, strong union between
chitosan particles was obtained through acetic acid rinsing, which partially dissolved the
surface. Scaffold porous architecture is presented in the pictures. The average porosity
measured was about 40% [30]. On the other hand, packing of microspheres and their
aggregation can be realized at high temperature. Briefly, chitosan-based microspheres are
put into a stainless-steel mold. The mold was heated to a temperature above the glass
transition of polymer for a certain time period to achieve bonding between adjacent
microspheres. The bonding of chitosan microspheres was achieved due to the bioadhe-
sive character of the chitosan polymer that resulted in the union of adjacent particles at
Figure 9.6
(a) Morphology of scaffold manufactured by the presented method. (b) SEM microphotograph of agglomerated
scaffold. (c) Spheres interconnectivity observed by optical microscope. (d) One of cross-sections obtained by
µCT scanning.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search