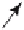Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
y
y
L
3
L
3
L
2
L
2
p
2
(4,4)
p
2
(4,4)
p
3
(0,0)
x
p
3
(1,0)
p
1
(4,-4)
p
1
(4,-4)
L
1
L
1
(b)
(a)
y
L
3
L
2
p
2
(4,4)
x
p
1
(4,-4)
p
3
(-1,0)
L
1
(c)
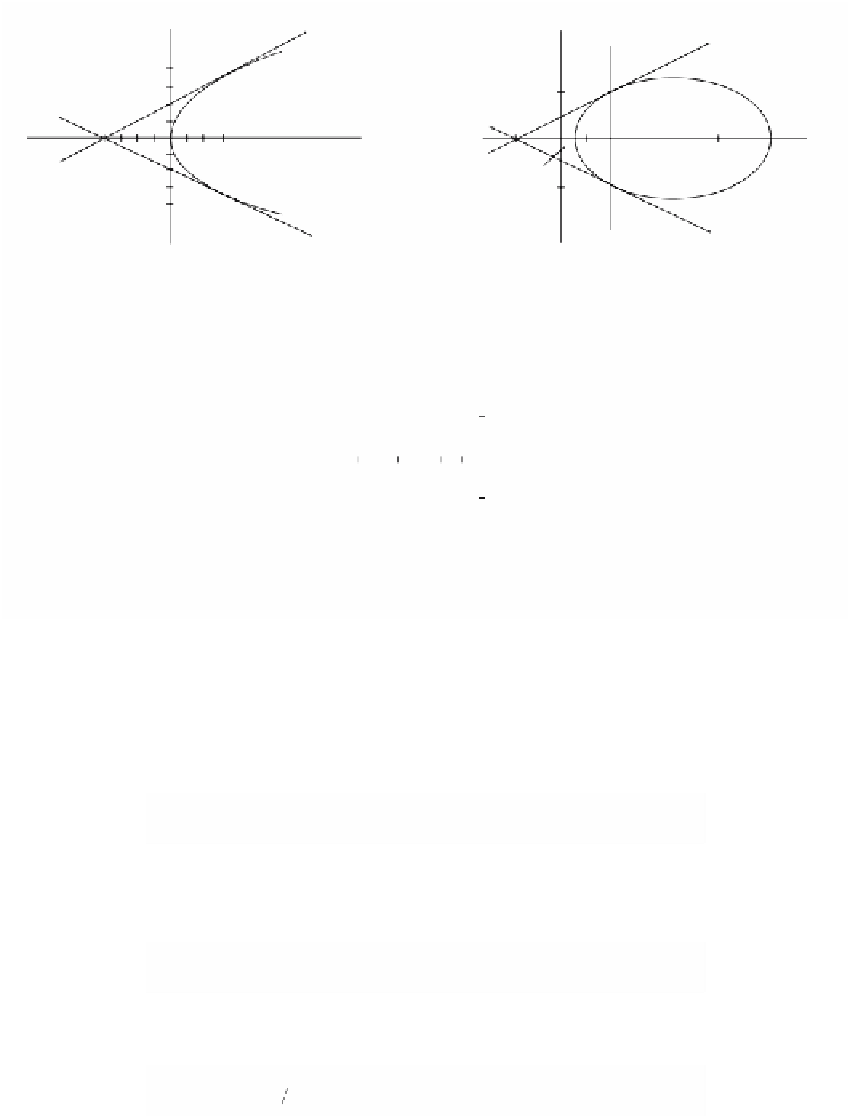
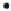
Figure 3.26.
The conics that solve Example 3.6.1.7.
and
4
2
(
)
=-+
(
)
(
)
+-
(
)
(
)
Cxy
,
l
x y
24 241
x y
++
l
x
-
.
l
Case p
3
= (0,0): See Figure 3.26(a). The equation C
l
(0,0) = 0 leads to the impos-
sible condition l = 0. This corresponds to the case l=•. Therefore, the conic we are
looking for is the parabola
2
•
(
)
=- +
(
)
(
)
--
(
)
2
Cxy
,
x y
24 24
x y
++
x
4
=-
y
4
x
.
Case p
3
= (1,0): See Figure 3.26(b). The equation C
l
(1,0) = 0 leads to the solu-
tion l=-9/16. This time our conic is the ellipse
(
)
=-++=
2
2
Cx y
,
4
x
68
x
9
y
64
0
.
-
916
Case p
3
= (-1,0): See Figure 3.26(c). The equation C
l
(-1,0) = 0 leads to the solu-
tion l=25/16. This time our conic is the hyperbola