Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(4.94)
4.7.2 Heteroatom Species
Different from hydrocarbons, heteroatom
compounds are oxidizable since they have lone
paired electrons on the heteroatom, from which
electron transfer occurs. In general, ease of
oxidation has the order N > S > O, and a variety
of nitrogen active species are generated
electrochemically [28].
4.7.2.1 Nitrogen Species
One-electron oxidation of amine generates a
radical cation at the nitrogen atom. The radical
cation of aromatic amine is relatively stable,
while that of aliphatic amine is so unstable that
the α-proton is immediately eliminated, and
then the active site shifts to the α-carbon. In the
case of ordinary aliphatic amines, iminium ions
are so unstable that cleavage of the C-N bond
occurs predominantly. On the other hand,
iminium ions of aromatic amines, carbamates
and amides are stable, therefore nucleophilic
substitution reactions like methoxylation,
acetoxylation and cyanation occur efficiently at
the α-position to the nitrogen atom, as shown in
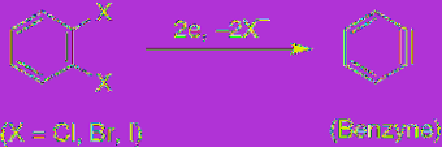
Search WWH ::

Custom Search