Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
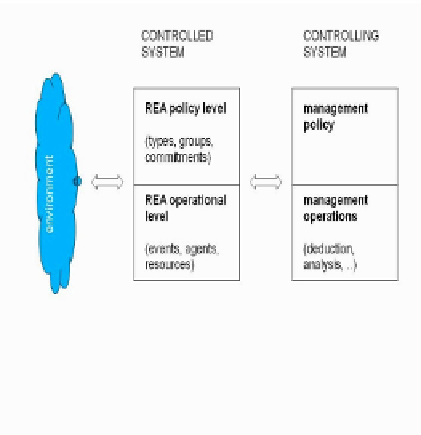
Fig. 1.
REA leve
els of controlled enterprise system, derived from [22]
The event records give a
the question “what is plann
modeled at the policy level
as commitments. Although
commitments are given, exa
and integrity constraints in
REA that makes a distinctio
1). The controlling system
toring the facts at the oper
etc at the policy level. As e
tem of the enterprise, so it d
an answer to the question “what has happened?”, but no
ned or scheduled - what
should
happen?” In REA thi
l. This level allows talking about types and groups as w
h no specific details for the structure of these types
amples in [5] show how REA does handle schedules, pl
n this way. [22] gives an enterprise architecture based
on between controlled system and controlling system (F
interacts with both levels of the controlled system, mo
ational level and changing the plans, standards, schedu
explained by [22], the controlling system is also a subs
does also have an operational and policy level.
ot to
is is
well
and
lans
d on
Fig.
oni-
ules
sys-
3.2 REA Management O
Ontology
The business ontology of R
enterprise on an abstract ec
level have not been worked
(types, groups) on the one
basket “policy level” is not
how commitments are crea
clear business impact and c
distinction between control
what exactly is processed
analysis, etc. Therefore we
tology”) that we will use as
The lower left corner su
(at operational level) as we
We group them together
“referred” to in
intentional
distinguished on the basis
directives
and
evaluatives
.
curred, whereas a directive
defined as having a world
ments that were already in
REA is strong in formalizing the operational level of
conomic level. However, the later extensions on the pol
d out as thoroughly. The occurrence of general abstracti
e hand and commitments on the other hand in the sa
t really satisfactory. The dynamics of this policy level,
ated and resolved, are also not covered, although this ha
cannot be left out of scope. The work of [22] adds a use
led system and controlling system, but it does not spell
in the controlling system when it talks about deducti
e have developed an extension of REA (“management
a basis for our design framework (Fig.2).
ummarizes the REA concepts of resource, event and ag
ell as types and groups (of resources, events and agen
under the category
REA referent
. REA referents
l resources
. Three categories of intentional resources
of what Searle [18] has called direction-of-fit:
assertiv
An (basic) assertive says that some REA event has
e says that some REA event should occur. Directives
-to-word fit and as such are a generalization of comm
n the REA business ontology, as part of the policy le
the
licy
ions
ame
e.g.
as a
eful
out
ion,
on-
gent
nts).
are
are
ves
,
oc-
are
mit-
vel.