Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
hypothesis
is evaluated on a sample data. One can distinguish between two
classes of hypothesis tests (i) tests on a single population (single-sample tests)
and (ii) tests on two populations (two-sample tests). Another classification of
hypothesis tests is concerned with the dimensionality of each data element in
a sample. Tests dealing with scalar data elements are called as
univariate
tests
while those dealing with vector data elements are called as
multi-variate
tests.
For our problem,
two-sample univariate and multi-variate tests are appropriate
.
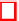
The dataset
of feature values can be considered as a time series as depicted
in Fig. 3. Each
d
i
∈D
D
corresponds to a feature value for a trace (or sub-log)
andcanbeascalaroravector.
The basic idea is to consider a series of suc-
cessive populations of values (of size
w
) and investigate if there is a significant
difference between the two populations
. The premise is that differences are ex-
pected to be perceived at change points provided appropriate characteristics
of the change are captured as features. A moving window of size
w
is used
to generate the populations. Fig. 3 depicts a scenario where two populations
P
1
=
of size
w
are considered.
In the next iteration, the populations correspond to
P
1
=
d
1
,
d
2
,...,
d
w
and
P
2
=
d
w
+1
,
d
w
+2
,...,
d
2
w
d
2
,
d
3
,...,
d
w
+1
and
P
2
=
d
w
+2
,
d
w
+3
,...,
d
2
w
+1
. Given a dataset of
m
values, the number of
population pairs will be
m
−
2
w
+1.
Iteration
2
Iteration
1
P
1
P
2
d
1
d
2
...
...
d
w
d
w
+1
d
w
+2
...
d
2
w
d
2
w
+1
...
...
d
m
Fig. 3.
Dataset of feature values considered as a time series for hypothesis tests.
P
1
and
P
2
are two populations of size
w
We will use the univariate two sample
Kolmogorov-Smirnov
test (
KS
test) and
Mann-Whitney U
test (
MW
test) as hypothesis tests for univariate data, and
the two sample
Hotelling
T
2
test for multivariate data. The
KS
test evaluates
the hypothesis “Do the two independent samples (populations
P
1
and
P
2
)rep-
resent two different cumulative frequency distributions?” while the
MW
test
evaluates the hypothesis “Do the two independent samples have different dis-
tributions with respect to the rank-ordering of the values?”. The multi-variate
Hotelling
T
2
test is a generalization of the
t
-test and evaluates the hypothesis
“Do the two samples have the same mean pattern?”. All of these tests yield a
significance probability
assessing the validity of the hypothesis on the samples.
We refer the reader to [13] for a classic introduction to various hypothesis tests.
5 Case Study and Discussion
We illustrate the concepts presented in this paper with an example process. The
process corresponds to the handling of health insurance claims in a travel agency.
Upon registration of a claim, a general questionnaire is sent to the claimant. In
parallel, a registered claim is classified into a high or low claim. For low claims,