Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Object Management Group's(OMG) metamodeling architecture called Meta-
Object Facility (MOF) [14]. MOF comes with a meta-meta model (M3 layer)
that allows us to define the structure, i.e. the abstract syntax, of the REA DSL
as a meta-model (M2 layer). The resulting REA DSL meta-model comprises
three interlinked views, of which we describe in detail the
duality
and the
value
chain
perspective. Due to space limitations, we do not elaborate in detail on the
third view on economic resources. However, it is important to note that economic
resources - scarce objects having utility and under control of an enterprise [15]
- may form a generalization hierarchy.
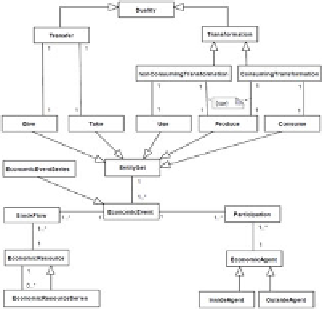
3.1 The Duality Model
The duality relationship is a core concept in REA. It links an increment in the
resource set with a corresponding decrement; where increments and decrements
must be members of two different event entity sets. In the REA ontology, the
duality relationship is characterized by the unary relationship assigned to the
concept of an economic event (see Figure 3(a)).
Duality
Transformation
Transfer
Transformation
nonConsuming
Transformation
Consuming
Transformation
nonConsumingTransformation
ConsumingTransformation
E1
R1
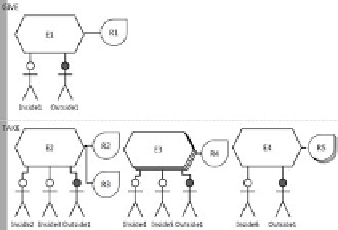
Give
Ta ke
Use
Produce
Consume
Economic
EventSeries
Entity
Set
EntitySet
Inside1
Outside1
Stock
Flow
Economic
Event
Participation
StockFlow
Participation
E4
E2
R2
E3
R5
R4
Economic
Resource
Economic
Agent
EconomicResource
EconomicAgent
R3
Economic
ResourceSeries
Inside
Agent
Outside
Agent
EconomicResourceSeries
InsideAgent
OutsideAgent
Inside2 Inside3 Outside1
Inside4 Inside5 Outside1
Inside6
Outside1
(a) Meta Model
(b) Example
Fig. 3.
Duality
In the REA DSL,
duality
becomes a core model element that serves as a
building block for further purposes. The duality meta model is depicted in Figure
3(a). Figure 3(b) presents a (rather abstract) example model - which should help
understanding the meta model concepts and to introduce the concrete syntax
and the corresponding stencils.
The
duality
concept applies to
transfers
(exchanges with external actors) and
transformations
(value creation inside the enterprise). In the case of
transforma-
tions
we distinguish between
resource-consuming
and
non-resource consuming
transformation
. As a consequence, the meta model defines
consuming transfor-
mation
and
non-consuming transformation
as special kinds of
transformation
as
well as
transfer
and
transformation
as specializations of
duality
.