Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
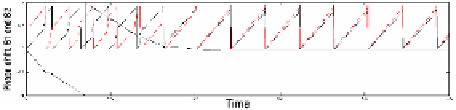
Fig. 8.
Signals of two agents and their associated phase-shift
Δ
φ
1
,φ
2
(
t
). When agents synchro-
nise with each other, their phase-shift remains constant and near zero.
between signals, i.e. synchronisation. Horizontal plate aux near zero reflect periods of
synchronisation and co-occurrence of non-verbal signals.
Finally, for each 5000 time steps simulation, we define that in-phase synchronisation
occurs if the phase-shift becomes near zero at a time
t
synch
, smaller than
3000
,andre-
mains constant until the end. We defined the synchronisation speed as
SynchSpeed
=
(3000
t
synch
)
/
3000
. If in-phase synchronisation is immediate
SynchSpeed
=1
;if
in-phase synchronisation occurs at time step 3000
SynchSpeed
=0
; and if in-phase
synchronisation do not occurs
SynchSpeed <
0
.
−
3.3
Test of Architecture Parameters
We tested different parameters of this model, first to show the direct link existing be-
tween emergence of synchrony and level of sharing between interactants, and second to
characterise the different properties of this model.
To show the direct link existing between emergence of synchrony and level of shar-
ing between interactants, we fixed
u
1
to
0
.
01
and made
u
2
vary between
0
and
0
.
02
,
that is to say the shared understanding of the two agents differs between
0
and
100%
.
Notice here the importance to test synchronisation when
u
2
=0
: if synchronisation
occurs when
u
2
=0
, i.e. when Agent2 does not perceived the speech of Agent1, that
means that agents synchronise every time just thank to non-verbal signal of Agent1; in
that case, synchrony is not any more an in dice of the interaction quality, the influence
of non-verbal signals (linked to
β
and
σ
) is too high.
To evaluate the influence of the amount of non-verbal signal exchanged, we made
the threshold
β
vary between
0
and
0
.
95
.
To evaluate the influence of the sensitivity to non-verbal signal, we made the sensi-
tivity
σ
vary between
0
and
0
.
09
.
Finally, to evaluate the abilities of such a dyad of agents to re-synchronise after an
induced phase-shift or after a misunderstanding, we made the initial phase shift
Δφ
ini
vary between
0
and
π
.
Shared Understanding Influence.
When the two agents are synchronous in phase
(
Δφ
ini
=0
), we tested which of the
u
2
values keep agents synchronised or make
them disynchronise. For fixed
β
=0
.
7
,
σ
=0
.
05
and
Δφ
ini
=0
,
u
2
varies between
0
and
0
.
02
. The following graph of Fig.9 shows the associated disynchronisation speed.
When the difference between
u
1
and
u
2
is to high, no synchronisation can oc-
cur since even when synchrony is forced at the beginning of the experiment, agent
disynchronise.