Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
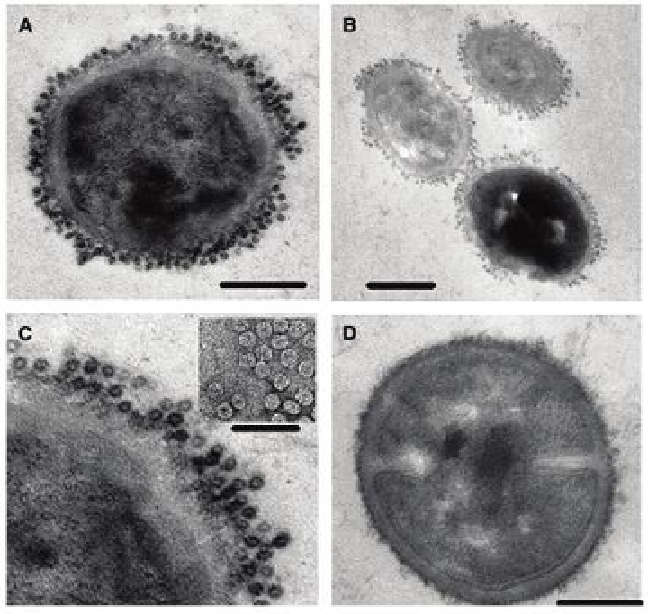
Figure 8.10
TEM thin sections showing high-density coverage of
Cowpea chlorotic
mottle virus
(CCMV) targeted to
Staphylococcus aureus
cells (a, b). Biotinylated
= CCMV-biotin (CCMV-B) bound to
S. aureus
cells via the StAv/anti-SpA mAb-B
linkage: the linkage consist of a biotinylated
-specific antibody that is linked
via streptavidin to the biotinylated CCMV particle. The scale bars in (a) and (b) are
200 and 400 nm, respectively. (c) Magnified view of image presented in (a) with an
insert of a TEM image of CCMV-B adsorbed on Formvar presented at the same scale
as the thin section. The scale bar is 100 nm. (d) Representative image of an
S. aureus
cell from the negative control indicating a negligible level of non-specific binding.
The scale bar is 200 nm. Reproduced with permission from Suci, P. A., Berglund,
D. L., Liepold, L., Brumfield, S., Pitts, B., Davison, W., Oltrogge, L., Hoyt, K. O., Codd,
S., Stewart, P. S., Young, M., and Douglas, T. (2007) High-density targeting of a viral
multifunctional nanoplatform to a pathogenic, biofilm-forming bacterium,
S. aureus
Chem.
Biol.
,
14
(4), 387-398.
Small drug molecules can be covalently attached or encapsulated
within VNPs. The chemotherapeutics hygromycin and doxorubicin have
been covalently attached to M13. Attachment was at the main coat protein
pVIII. Targeting was achieved via presentation of antibodies against ERGR
and ErbB2 (both are receptors that are overexpressed on tumor cells); the
antibodies were attached to the minor coat protein pIII. Cancer-cell-specific
targeting and cell killing were confirmed
in vitro
(Bar
et al
., 2008).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search