Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
On the basis of water vapor isotherm, we can find three sorption modes. The first
concave part of the curve indicates Langmuir-type adsorption behavior assuming a
sorption on specific sites or micro-voids inside polymer (free volume). The follow-
ing linear part of the isotherm corresponds to a Henry-type process involving random
adsorption by dissolution and diffusion of the water molecules inside polymer. The
combination of Langmuir-type and Henry-type sorptions is commonly attributed to
the dual-mode sorption in glassy polymers. The convex part of the curve corresponds
to sorption of water molecules leading to the water clustering formation. Usually
the combination of dual mode sorption with aggregation sorption corresponding to
Park's model was typical of water sorption in hydrophilic polymers. In general, the
water sorption behavior in hydrophilic material is analyzed from BET (Brummer-Em-
met-Teller) isotherm, and in particular GAB (Guggenheim-Anderson-de-Boer) model.
Water and Gas Permeation
The permeation properties of polymer film were studied with methods appropriate to
the nature of the diffusing molecules. The water and gas diffusing molecules perme-
ation measurements can also be performed from different techniques.
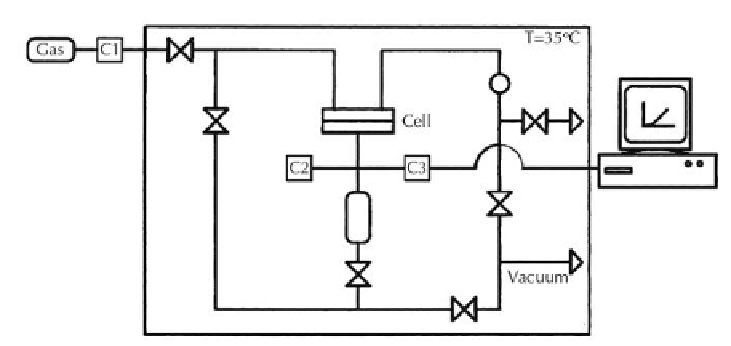
The gas molecules permeation measurements were carried out generally by the
“time-lag” method, a variable pressure method, by using the permeation apparatus
shown in Figure 6. The permeability coefficient, expressed generally in Barrer (10
-10
cm
3
STP cm/cm
2
s cmHg), was calculated from the slope of the steady state line im-
parting the saturation level by taking into account the exposed area of the film and the
vapor pressure difference across the two sides of the film.
A preliminary high vacuum desorption was realized on both sides of the perme-
ation cell. Then the upstream compartment was filled with gas at determined pressure.
In the downstream compartment, the increase of pressure was measured as a function
of time by using a datametric pressure sensor communicating with a data acquisition
system.
Figure 6.
Apparatus based on a barometric permeation method (Joly, 1999).


Search WWH ::

Custom Search