Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
60
T-23
T-24
t
= 1 d
50
40
t
= 2 d
t
= 3 d
t
= 4 d
30
20
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
Depth (
z
), m
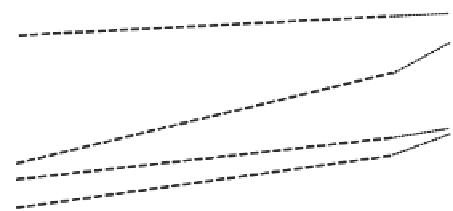
Figure 7.39
Volumetric water content profiles of Test SM1-T1 based on SWCC and pore-water
pressure data measured on tensiometers T-23 and T-24 during drying process (after Krisdani et al.,
2009).
10
-5
Drying permeability function calculated using statistical
method based on drying SWCC and
k
s
= 9.0
×
10
−
7
m/s
10
-6
10
-7
10
-8
10
-9
10
-10
10
-11
Coefficient of permeability obtained
from instantaneous profile method
10
-12
0.1
1
10
100
1000
10,000
100,000
Matric suction (
u
a
-
u
w
), kPa
Figure 7.40
Permeability function for RS computed using instantaneous profile and statistical
method (after Krisdani et al., 2009).
function for the unsaturated soil. Obtaining the correct satu-
rated coefficient of permeability appeared to be the greatest
challenge.
extent as laboratory tests. Also, laboratory tests cost less
than field tests. These are the main reasons why most testing
has been performed in the laboratory.
The instantaneous profile method is generally considered
to be the best method for permeability testing in the field
(Klute, 1972). The procedure used in the field is similar in
concept to the instantaneous profile method described for
the laboratory.
The advantage of the in situ instantaneous profile method
is that relatively simple equipment is required. The method
is not applicable when there is significant water flow in the
horizontal direction. Horizontal flow may occur as a result
of either a low-permeability layer or a highly permeable
7.6.3.4 In Situ Instantaneous Profile Method
Nonhomogeneity and anisotropy of soils in the field make in
situ measurements for the coefficient of permeability superior
to laboratory measurements. Fissures, fractures, tension
cracks, and root holes commonly encountered in unsaturated
soils cannot be properly represented in small-scale laboratory
specimens. Furthermore, laboratory specimens are subjected
to sampling disturbance. On the other hand, in situ
permeability tests have not been developed to the same
































Search WWH ::

Custom Search