Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
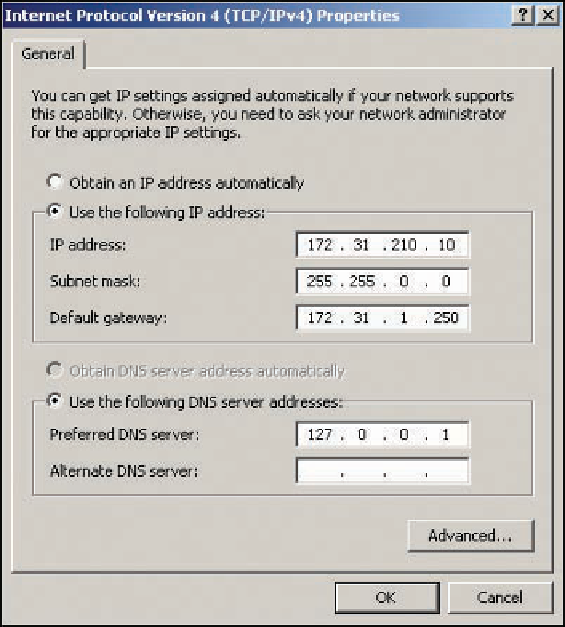
By doing so, the computer can determine on which network it is located. When a packet is sent
to a destination computer, the computer compares its own network ID to the destination net-
work ID. If they differ, the packet must be sent to a router. In Figure 8-6, the network ID of the
IP address is 172.31, and the host ID is 210.10.
8
Figure 8-6
The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties dialog box
Assigning IP Address Classes
When you enter an IP address in the Properties
dialog box shown in Figure 8-6, Windows fills in a subnet mask automatically, which you
can change if necessary. Windows bases the suggested subnet mask on the class of the IP
address you enter. Three classes of IP addresses can be assigned: class A, class B, or class C.
The class to which an IP address belongs is determined by the value of the address's first
octet, as shown in Table 8-1.
Table 8-1
IP address classes
Value of first octet
Class
1-127
A
128-191
B
192-223
C
There are also class D and E addresses, which can't be assigned to hosts.
Class D addresses, with the first octet in the range 224 to 239, are used
for multicast applications. Class E addresses, in the range 240 to 255, are
reserved for experimental use.




Search WWH ::

Custom Search