Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
1. Log on to your server as Administrator, if necessary.
2. Click
Start
, and then right-click
Computer
and click
Explore
.
3. Right-click the
(C:)
drive in the right pane and click
Properties
.
4. Click the
General
tab, if necessary. Verify that NTFS is listed for the file system. If the drive
isn't formatted as NTFS, ask your instructor which drive is formatted as NTFS on your
system and repeat from Step 3.
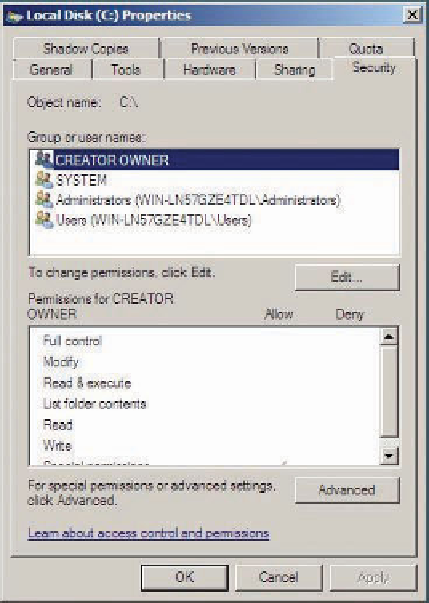
5. Click the
Security
tab (see Figure 1-1).
1
Figure 1-1
The Security tab showing NTFS permissions
6. Click each item in the Group or user names list box, and view the permission settings for
each at the bottom.
7. Next, click the
Quota
tab. Quotas, a feature available only on NTFS-formatted disks, are
discussed more in Chapter 6.
8. Now click the
Shadow Copies
tab. This feature is yet another one that requires NTFS.
9. Last, click the
General
tab again. Note the two check boxes at the bottom for enabling indexing
and compression. NTFS volumes allow these features, which aren't available with FAT volumes.
10. Close the Properties dialog box.
11. Click the
Documents
icon under Favorite Links. Right-click the right pane, point to
New
,
and click
Text Document
. Press
Enter
to accept the default filename New Text Document.
12. Right-click
New Text Document
and click
Properties
. Notice the two check boxes at the
bottom next to Attributes. They are common file attributes in both the FAT and NTFS file
systems. Click the
Advanced
button.
13. In the Advanced Attributes dialog box, notice four more check boxes for attributes. Only
the archiving attribute is available with FAT volumes. The other three, for file indexing, file
compression, and encryption, are available only with NTFS volumes.
14. Close all open windows.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search