Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
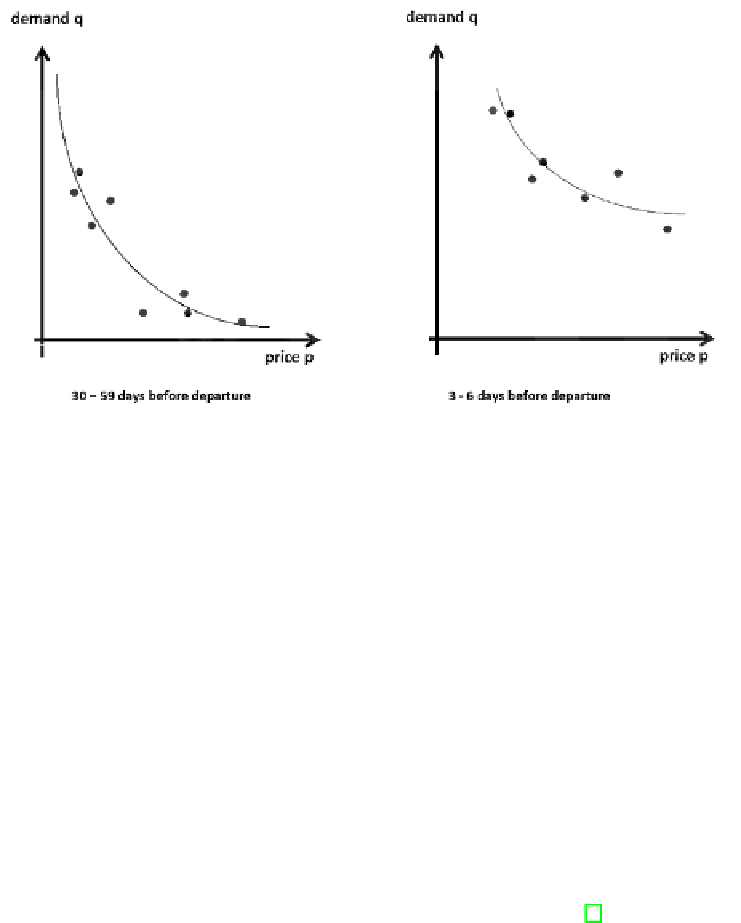
Fig. 1.
Exemplary market-response-functions
Based on these forecasts, the optimization module of RM has to determine for
each time interval a set of price/capacity pairs as basis for a fare class control,
which is then implemented by the online booking system.
Since pricing has become the only mechanism to shape, the demand pat-
tern fine-grained approaches respecting specific and small price differences are
necessary. Since generating valid forecasts is not always possible, especially un-
der changing markets with new relations and competitors, LCC need highly
responsive RM systems where both forecasting and optimization are frequently
recalculated. Also, the system should allow interactivity, i.e., manual corrections
of booking limits in light of the actual booking situation. In the next section we
focus on the optimization module of a RM system for LCC.
3 Optimization Models
At the heart of the RM-optimization model is a revenue function which is to
be maximized subject to a capacity constraint as described in [7]. They assume
that the reference time unit is a single day, i.e., demand and price are fixed over
a single day. Then, considering a booking period of
N
days we have to determine
aprice
p
i
and a capacity
q
i
for each day
i
.Letthe
aircraft/flight capacity be
Q
then the model in the notation of [7] is as follows:
max
i∈T
∈
T
, with
T
:=
{
1
,
2
,
3
, ..., N
}
s.t.
i∈T
p
i
q
i
q
i
≤
Q
[7] show how this model can be solved for different functional forms of the
demand curve
q
i
=
q
i
(
p
i
) by analyzing the derivative of the associate lagrangian