Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
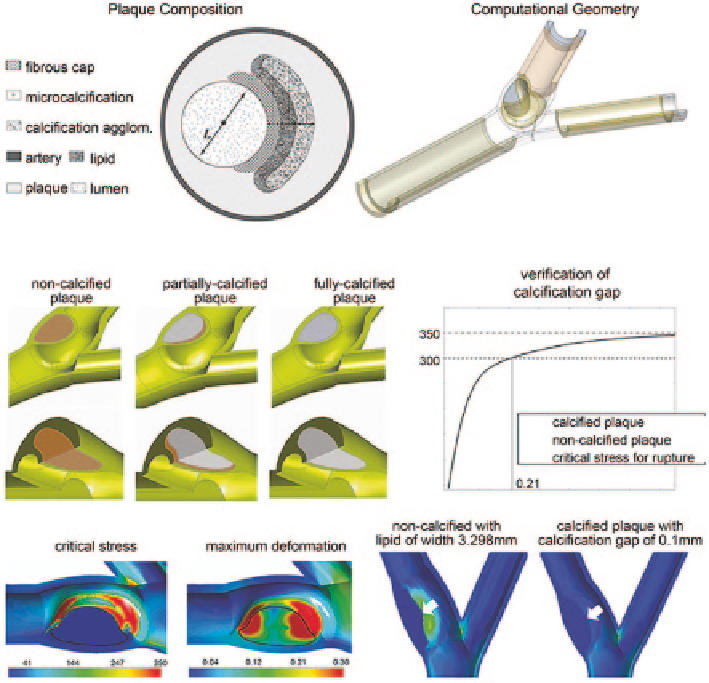
Fig. 1.8
Three-dimensional fluid and structural modelling of plaque. Computational haemody-
namics simulation of blood flow through atherosclerotic arteries and structural analysis of calci-
fied plaques with fibrous caps based on fluid structure interaction is implemented
Therefore, understanding the haemodynamics before and after carotid stenting is
of paramount importance in determining the need to deploy stents into the diseased
vascular regions. This can reduce future procedure-related complications such as
restenosis or occlusion that may occur unexpectedly. A simulation-based virtual
stenting platform can be implemented by multiple imaging, computational and vi-
sualization, as well as flow analysis modules as shown in Fig.
1.9
. This provides
clinical management, simulation of flow conditions due to cardiovascular diseases,
and planning of stent designs.
MRI scans can demonstrate the obliquity of stenosed arteries. Its treatment by a
virtual stent design can be produced based on a B-Spline interpolation technique.
The results from simulations of virtual stenting of a stenosed artery is shown in
Fig.
1.10
where flow patterns become regular since there is no stenotic section in the
artery which interferes with blood flow. Low wall shear stress (of low magnitudes
Search WWH ::

Custom Search