Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
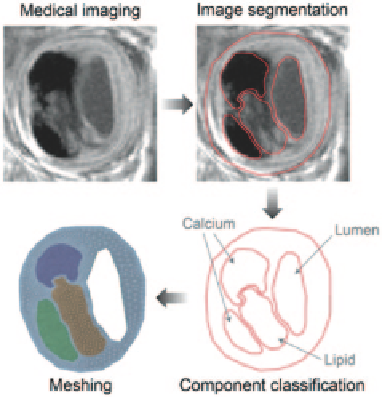
Fig. 1.7
Flow chart of proposed components for plaque vulnerability investigation. The stages
of plaque structural modelling which involves medical imaging techniques such as MRI imaging,
image segmentation (
discussed later in Chap� 3
), component classification by identifying their
intensities, and finally meshing (
discussed later in Chap� 4
)
bifurcation at 80 % degree of stenosis (by area) demonstrates the resistance force
on the plaque due to calcification. This reduces the maximum principal stress and
deformation in the artery. Plaque-rupture analysis based on critical stress of fibrous
cap for 3D plaque, (i.e plot of critical stress
σ
cr
versus width of calcification gap
d
cg
) shows that a calcification gap value of > 0.21 mm causes stress levels to exceed
300 kPa leading to plaque rupture.
Modelling of the human atherosclerotic artery with varying degrees of lipid core
elasticity, fibrous cap thickness and calcification gap, form the basis of a rupture
analysis. The results add new mechanistic insights and methodologically sound data
to investigate plaque rupture mechanics.
1.3.5
Preoperative Assessment of Atherosclerotic Arteries
Based on flow and patient specific information a system for decision and evaluation
of treatment based on CHD can be performed. By carrying out systematic simula-
tions of diseased vascular systems, appropriate treatment solutions can be formed.
Stenting has been well-established as the most feasible treatment for athero-
sclerotic lesions. It is becoming an alternative to traditional endarterectomy due to
its less invasive nature and high successful rate. However, the placement of stents
alters the haemodynamics and coupled with wall movement may lead to the dis-
persion of late multiple emboli (Richter et al. 1999). The complex structures intro-
duced into the blood flow may enhance biochemical thrombosis cascade (Beythien
et al. 1999; Peacock et al. 1995), as well as directly affecting local haemodynamics.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search