Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
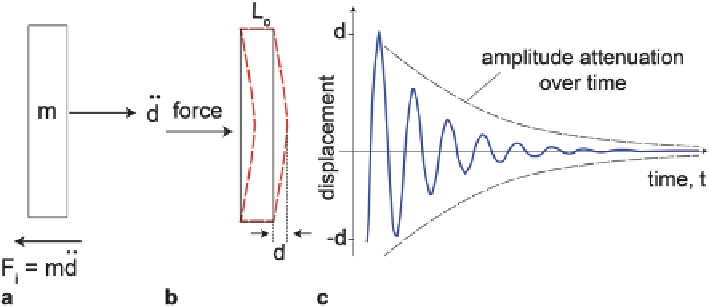
Fig. 5.19 a
Deformation of a vessel wall caused by an applied force develops an inertial force in
response to an applied load.
b
Upon release of the force the wall will deform towards its original
shape but may overshoot its original position giving rise to an oscillatory deformation.
c
The
damping force attenuates the oscillation with time
the finite volume approach that is often used for fluid flow equations (although fluid
flow can also be cast in finite element method). Equation (5.33) is rewritten with the
stiffness force replaced by a stress term, per unit volume to give
(5.34)
ρ
dd
+ +∇ =
c
·
σ
f
s
ij
ρ
is the density of the solid, and
i
σ
is the stress tensor with the divergence rep-
resenting internal elastic forces. The external force,
f
represents forces induced by
blood flow that includes fluid pressure and shear.
The relationship between the stress tensor and deformation (i.e. strain) represents
the constitutive behaviour of the vessel wall. This may be linear or non-linear de-
pending on the material. In general the relationship is of the form
ij
σ =
where
D
is the constitutive elastic stiffness matrix (typically a function of the material
elasticity, Young's modulus, and Poisson ratio), and
i
ε
is the strain tensor. In-depth
descriptions of these relationships are given in Xia and Lin (2008) and Zienkiewicz
and Taylor (2000).
D
ij
5.3.4
Elastic Properties of Arteries
Arteries carry blood from the heart, which exhibits high pressure, while veins con-
duct blood from the capillaries back to the heart which have lower pressure. These
pressure forces act on the vessel walls causing elastic deformation. During systolic
phase, healthy arteries expand, and absorb the peak systolic pressure. During dias-
tole the blood pressure reduces and the vessel walls return to their original form to
maintain the flow. When arteries become diseased, such as arteriosclerosis, they
become stiffer, and lose the ability to deform freely, increasing pressure at peak
systolic phase.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search