Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
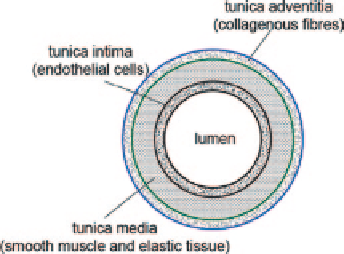
Artery walls are made up of four types of tissues, (i) endothelial cells, (ii)
connective elastic and collagenous fibres, (iii) smooth muscle, and (iv) irregular
connective elastic and collagenous fibres. These are found within three layers: the
tunica intima (inner), the tunica media (middle), and the tunica adventitia (outer).
Figure
5.20
shows a schematic of the artery wall structure and composition of tis-
sues within each of the three layers. It also shows the relative tissue composition
within each artery type. The tunica intima consists of endothelial cells; the tunica
media is the middle layer and is composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibres; and
the tunica adventitia contains connective collagenous fibres that anchor the blood
vessel to nearby organs, giving it stability.
The amount and composition of different tissues in the artery varies based on the
artery size and this determines its elasticity. More elastin in the arteries allows them
to expand and contract. Accordingly the arteries are either predominatly muscular or
elastic. The aorta and larger arteries contain more elastin which stretches as the blood
is forced into the artery. The deformed artery holds this energy (like the stiffness
constant,
k
in Eq. (5.33)) and during diastole releases this energy, recoiling back to its
original shape during diastole to propel the blood forward. The ability to absorb the
peak systolic pressure dampens sudden loads on the artery wall. Arterioles contain
less elastin and more smooth muscle which make the walls more rigid and stiff.
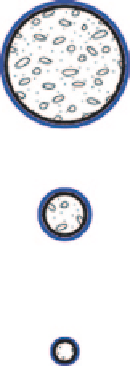
Relative Tissue
Composition
Vessel Type
elastic artery
muscular artery
arteriole
a
b
Fig. 5.20
Arterial wall has a three-layered anatomy made up of tunics—tunica intima, tunica
media, and tunica adventitia. The intima consists of endothelial cells, the media consists of smooth
muscle and elastic tissue, and the adventitia consists of collagenous fibres. Larger arteries are
typically elastic containing a larger relative composition of elastin, while smaller arteries are pre-
dominantly made up of smooth muscle

Search WWH ::

Custom Search