Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
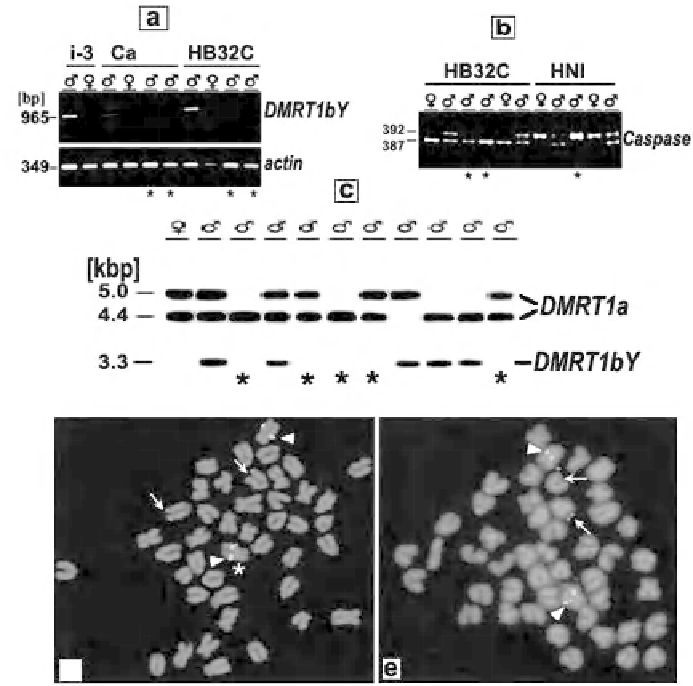
A
B
E
D
Fig. 10.
Oryzias latipes
: (A):
PCR genotyping of males and females. Note the presence of
Dmrt1bY
in normal males but its absence in aberrant females. (B): Hemizygosity of normal
males of the HB32C and HNI strains for
caspase
6. Females and aberrant males (*) show only
the X chromosomal PCR product. (C): Southern blot analysis of DNA from female, normal male
and aberrant (
Dmrt1bY
negative) males (*). FISH pattern of Y specifi c and sex chromosome
specifi c probes on (D) XY and (E) XX metaphase chromosomes. Note the presence of three
hybridization signals in XY males, as compared to two spots in XX males (from Nanda et al.,
2003, with permission by the Genetic Society of America).
Color image of this figure appears in the color plate section at the end of the topic.
other three localities yielded both male and female XY
m
progenies. Hence
all these wild XY females had Y-linked mutations.
Screening for Y-linked mutations in amino acid coding sequence of
DMY
(Fig. 11) and examining
DMY
expressions at 0 dph with densitometric semi-
quantitative RT-PCR, Otake et al. (2006) classifi ed the mutations into two
groups: one containing mutations in the amino acid coding sequence and
the other showing reduced
DMY
expression (cf Herpin et al., 2007), although