Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
From 1 to 2 ml of 5 ml inoculum was retrieved by rotating
the animal from side to side several times and applying
gentle pressure to the thorax during aspiration. Fluoroscopy
can also be used with this technique to visualize the exact
location of the lavage and aspiration (
Hannothiaux et al.,
1991
).
One method for obtaining bacterial cultures and cyto-
logical samples for diagnosis of respiratory disease is
tracheobronchial wash. Stills and colleagues reported on
a method in cynomolgus monkeys (
Stills et al., 1979
). The
monkeys were restrained in an upright position with the
head and neck in complete extension so as to facilitate entry
into the trachea. A 17- or 19-gauge intravenous catheter and
needle set was pierced through the skin and into the
tracheal lumen between the cartilagenous tracheal rings.
The needle was withdrawn once the catheter was in
a bronchial lumen. To obtain the respiratory fluid sample,
10
emission or ejaculation was shown to occur when alter-
nating current is delivered at 0.25 mA/mm
2
electrode area
at a frequency of 20 Hz. Direct electrical stimulation of the
nonhuman primate penis has been described (
Sarason et al.,
1991
). The artificial vagina method of semen collection has
been successful for chimpanzees and orangutans (
Hardin
et al., 1974; Gould et al., 1985; VandeVoort et al., 1993
),
which may be due to their greater intelligence and ease of
training to new behaviors.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Collection Volume
There have been two commonly used guidelines for
maximum blood withdrawal in the field of nonhuman
primate medicine. One common recommendation is to
collect no more than 10% of the calculated normal blood
volume, roughly estimated to be 10% of body weight
(
McGuill and Rowan, 1989
). Another is that blood
collected over a 2-week period should not exceed 15% of
the total blood volume (
Fox, 2002
).
15 ml of sterile saline was introduced through the
catheter and then aspirated back immediately into the same
syringe. Typically 4 ml of the saline was recovered and
could be used for bacterial culture or centrifuged for
examination of any cellular sediment.
e
Venepuncture
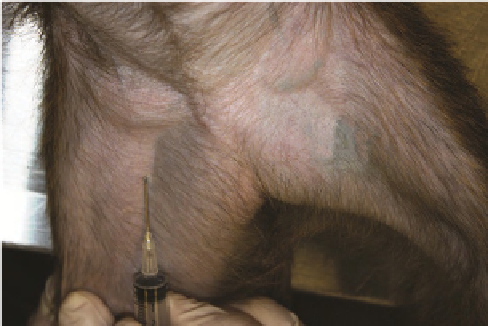
In nonhuman primates, the site most commonly chosen for
venepuncture is the femoral vein (
Figure 13.7
). It can be
used in very small up to very large animals and is usually
the largest readily accessible vessel. Other common sites
include the cephalic vein (
Figure 13.8
), saphenous vein,
lateral tail vein, and jugular vein.
The site chosen for blood draw is first shaved and then
prepped with an alcohol wipe. The alcohol will clean most
gross soilage and will make the vessel easier to see. Some
vessels can be seen readily; others will take some practice
to locate and may only be palpated. For instance, the
femoral artery cannot always be seen but the pulse can be
palpated in the groin region. Once the femoral artery is
Bronchoalveolar Lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) is a procedure in which
a bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into
the lungs and fluid is flushed into a small part of the lung
and then recollected for examination. BAL is the most
common manner to sample the components of the epithelial
lining fluid and to determine the protein composition of the
pulmonary airways. One report described performing BAL
in rhesus, cynomolgus, and African green monkeys using
a pediatric endoscope (
Tate et al., 2004
). Phosphate buff-
ered saline was infused through a sampling tube and then
suctioned using a medical aspirator into a sterile collection
vial.
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Semen Collection
The method of semen collection can have an impact upon
the quality of the sample collected (
VandeVoort, 2004
).
Semen may be collected by post-copulation vaginal washes
(
Kuederling et al., 1996
). A modified test yolk mediummay
be used for rinsing the vagina. The unsedated female is
manually restrained in an inclined head-down position and
the vagina is washed using a 0.5-ml disposable plastic
pipette, the tip of which is prolonged with a 2-cm-long and
2-mm-wide (outside diameter) piece of soft, flexible
silastic tubing. Electrical ejaculation with rectal probe is
another method to collect semen from many different
nonhuman primate species (
Gould et al., 1978
). Seminal
FIGURE 13.7
Location of the femoral vein in a small nonhuman
primate.