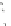Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
Reference or
Sample
Switch
Valve
A
Column
MS
B
Injection
Valve
Pump
LC
Precolumn
b
100
80
60
40
20
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
Time (min)
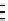
Fig. 4
Instrumental setup (
a
) and representative peaks (
b
) of echo-peak technique. An unknown
sample is first injected and the mobile phase flows directly to the separation column. Within a short
delay, a reference standard solution is injected and the switching valve turns to a different position
to allow the mobile phase to flow through a short precolumn (as shown by
dashed arrows
) prior to
passing through the same separation column. Two chromatographic peaks are therefore recorded,
one for the unknown sample (
solid line
) and the other for the reference solution (
dotted line
).
A and
B
mobile phases,
LC
liquid chromatograph,
MS
mass spectrometer
MS detection, such as using automated sample preparation, obtaining clean extracts,
and achieving good separation between the analyte and the coextracted matrix com-
ponents that could cause matrix effect.
In addition, a new technique termed ECHO peak technique could be considered
[
23,
24
]. With this new technique, two injections are carried out in each analysis,
namely within a short time period (typically 30-50 s) the unknown sample and a
standard solution. As a result, the peak of the analyte from the standard elutes in
close proximity to the peak of the analyte from the sample, thus forming the so-
called echo peak (Fig.
4
). It is expected that both peaks elute so closely that they are
affected in the same manner by the coeluted matrix components, which usually have