Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
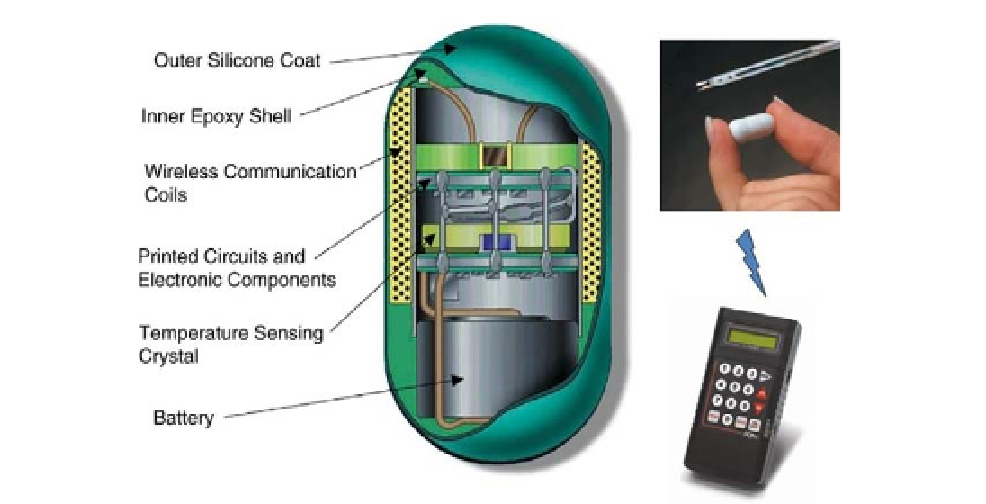
FIGURE 10.26
Ingestible temperature pill.
Courtesy of HQ, Inc., Palmetto, FL.
Traditionally, arterial blood gas analysis has been performed by withdrawing blood from
a peripheral artery. The blood sample is then transported to a clinical laboratory for analy-
sis. The need for rapid test results in the management of unstable, critically ill patients has
led to the development of newer methods for continuous noninvasive blood gas monitor-
ing. This allows the physician to follow trends in the patient's condition as well as receive
immediate feedback on the adequacy of certain therapeutic interventions.
Noninvasive sensors for measuring O
2
and CO
2
in arterial blood are based on the discov-
ery that gases, such as O
2
and CO
2
, can easily diffuse through the skin. Diffusion occurs due
to a partial pressure difference between the blood in the superficial layers of the skin and
the outermost surface of the skin. This concept has been used to develop two types of non-
invasive electrochemical sensors for transcutaneous monitoring of
CO
2
. Further-
more, the discovery that blood changes its color depending on the amount of oxygen
chemically bound to the hemoglobin in the erythrocytes has led to the development of sev-
eral optical methods to measure the oxygen saturation in blood.
p
O
2
and
p
10.4.1 Oxygen Measurement
A quantitative method for measuring blood oxygenation is of great importance in asses-
sing the circulatory and respiratory condition of a patient. Oxygen is transported by the
blood from the lungs to the tissues in two distinct states. Under normal physiological con-
ditions, approximately 2 percent of the total amount of oxygen carried by the blood is dis-
solved in the plasma. This amount is linearly proportional to the blood
O
2
. The remaining
98 percent is carried inside the erythrocytes in a loose, reversible chemical combination
with hemoglobin (Hb) as oxyhemoglobin (HbO
2
). Thus, there are two options for measur-
ing blood oxygenation: either using a polarographic
p
O
2
sensor or measuring oxygen satu-
ration (the relative amount of HbO
2
in the blood) by means of an optical oximeter.
p