Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
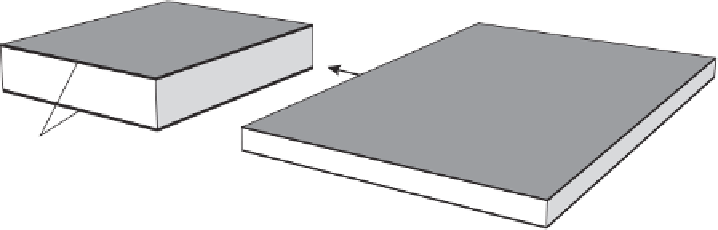
Elastic dielectric film
P
V
Compliant electrodes
P
Figure 7.3
Deformation of an elastic dielectric film under electrostatic pressure [15]
between carbon electrodes. Jungmann and Schlaak [15] used a stack of many layers
of dielectric films and electrodes to obtain the large absolute displacements depicted in
Figure 7.4.
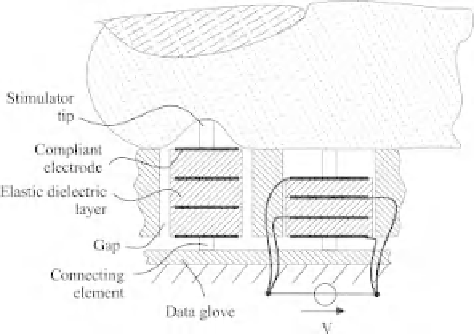
If a voltage (
V
) is applied between the neighboring electrode layers, the actuator stack
will contract and the stimulator tip will disappear below the surface of the device. To
ensure the area expansion, there has to be a gap around the actuator stack. By reducing
the voltage, the electrodes are discharged beyond the voltage source, causing a relaxation
of the actuator stack. As a result, the stimulator tip is pressed against the skin on top of
the device because of the stored elastic energy.
A stimulator with a relative strain of 30% at an absolute value of 4 mm would require
more than 1000 dielectric layers, 10 mm in thickness. This shows the necessity of automat-
ing the actuator processing [15]. In Figure 7.5, a possible stimulator arrangement for a
tactile display with elastomeric actuators is shown.
Figure 7.4
Structure and function of an electrostatic tactile stimulator with elastic dielectric [15]