Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
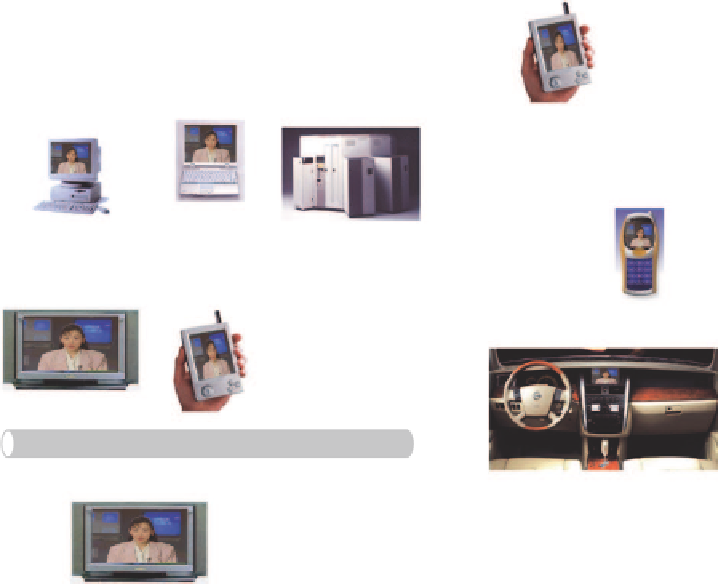
Broadcasting
Point-to-Point
Transmission
Server
128 kbps
64 kbps
Wireless
32kbps
512 kbps
384 kbps
Ethernet
Wireless
256 kbps
Router
1.5 Mbps
64 kbps
Ethernet
Bandwidth
3Mbps
Time
Fig. 3.1.
Application framework for Scalable Video Coding.
AVC/H.264-based approach [2]. In addition, and depending on the transform
order in the spatio-temporal domain, the wavelet-based scheme can be further
divided into two variations. That is the 2D+t(+2D) and t+2D structures
[2]. In order to distinguish the differences, Fig. 3.2 gives a comparison of the
architecture of these two variations.
To achieve temporal scalability, both the wavelet-based scheme and the
AVC-based approach adopt the technique of Motion Compensated Temporal
Filtering (MCTF). To achieve the SNR scalability with a fine granularity,
the AVC-based scheme uses a context-adaptive bit-plane coding [3, 4]. The
wavelet-based scheme employs an embedded quantizer with arithmetic cod-
ing [5, 6, 7] for the same purpose. For spatial scalability, the wavelet-based
scheme uses the advantages of multi-resolution property of wavelet transform.
The AVC-based scheme exploits the layered coding concept used in MPEG-2,
H.263, and MPEG-4.
A test has been done comparing these technologies [8]. The AVC-based
scheme has a better quality for several features and was adopted as the joint
ITU and ISO MPEG SVC standard draft. The MPEG committee also estab-
lished an ad-hoc group to further study wavelet-based technologies for possible