Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
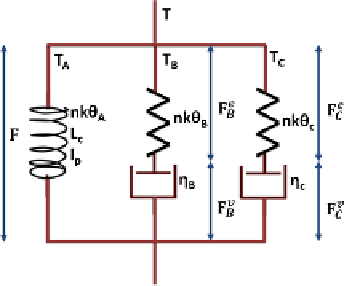
Fig. 25.4
Afive-element
nonlinear viscoelastic
constitutive model
The linear dashpot constitutive equation for the viscous element
B
,
C
is
D
B,C
=
T
B,C
/η
B,C
where
D
B,C
is the viscous shear strain rate,
η
B,C
is the constant shear
viscosity and
T
B,C
is the equivalent shear stress. The network deformation is as-
sumed to be incompressible. The model implementation and parameter determina-
tion will be presented in the next section.
25.3 Methods
25.3.1 Experimental Characterization of the ACL and Tissue
Engineered Graft
We have previously developed a tissue engineered bone-ligament-bone (BLB) con-
struct from bone marrow stromal cells and used it as a graft to replace the ACL in a
sheep model. A detailed description can be found in Ma et al. (
2012a
,
2012b
). After
9 months of implantation, the tissue engineered grafts and the contra-lateral ACLs
were dissected with the femur and tibia attached for mechanical testing. The femur
and tibia of each sample were fixed in a customized grip apparatus at a 30 degree
knee flexion angle and the entire unit was installed onto an MTS 810 servo hydraulic
test system with a 25 kN load cell. Uniaxial tension tests and stress relaxation tests
were conducted to characterize the material properties of the samples. High-speed
cameras were employed to measure the displacement at the tissue level. A speckle
pattern made from waterproof India ink was applied on the surface of the samples.
VIC-2D software (Correlated Solutions) was used for accurate tissue deformation
determination via digital image correlation analysis and full-field strain contours of
the tissue were obtained. The strain data of each test were then obtained by averag-
ing all the data points on the tissue surface.