Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
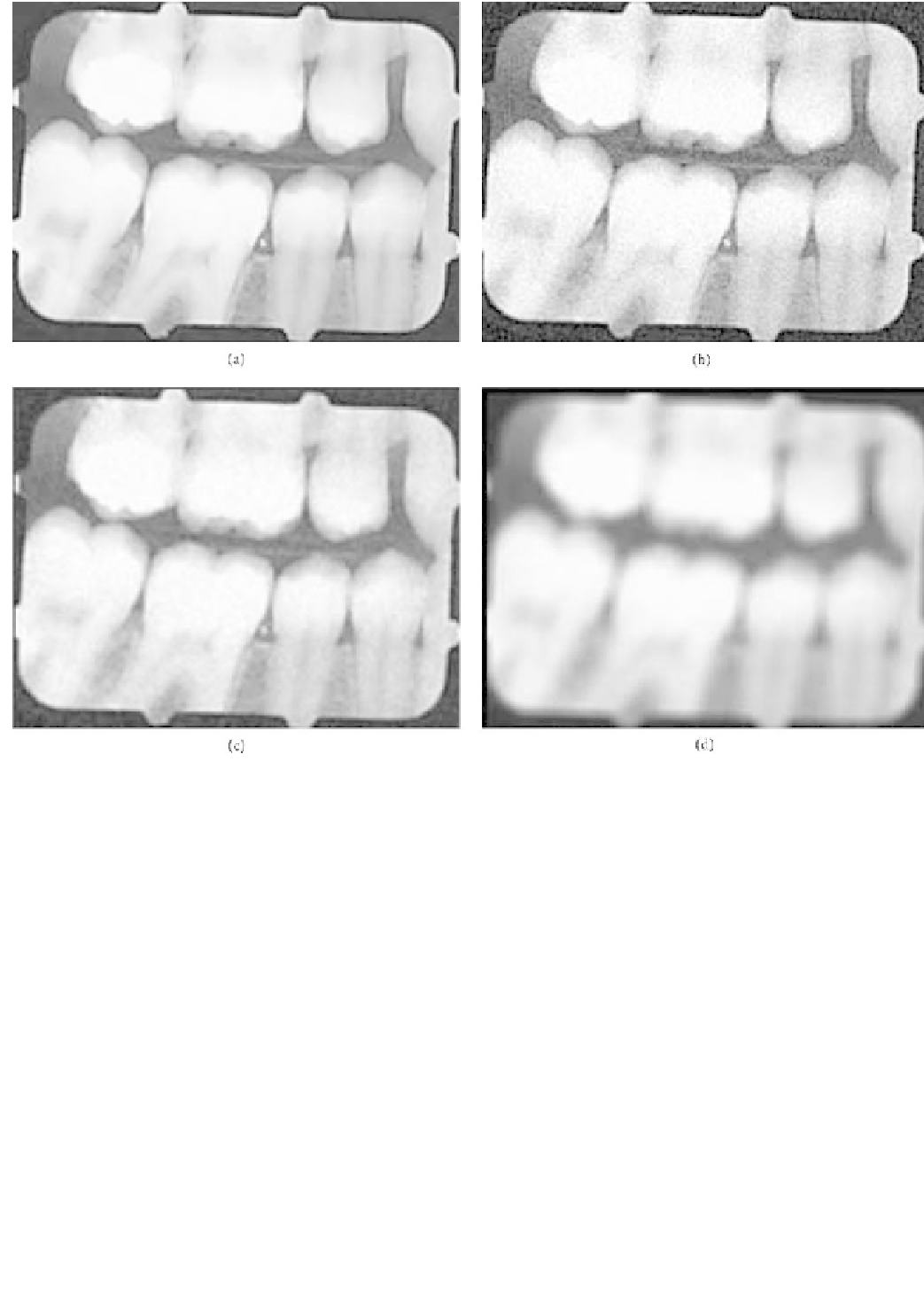
Figure 6.3-4 (a) Original bitewing X-ray image. (b) Original image in (a) corrupted by added Gaussian white noise with maximum
amplitude of 25 gray levels. (c) Image in (b) convolved with the 3 3 mean filter. The mean filter clearly removes some of the additive
noise; however, significant blurring also occurs. This image would not have significant clinical value. (d) Image in (b) convolved with the
9 9 mean filter. This filter has removed almost all of the effects of the additive noise. However, the usefulness of this filter is limited
because the filter size is similar to that of significant structures within the image, causing severe blurring.
nonlinear operation of the median filter allows significant
reduction of specific types of noise. For example, ''shot
noise'' may be removed completely froman image without
attenuation of significant edges or image characteristics.
Figure 6.3-5
presents typical results of median filtering.
Horizontal edges and lines are enhanced with
(
111
000
1
1
1
)
w
H
1
ðk; lÞ¼
or
w
H
2
ðk; lÞ¼
(
1
1
1
)
000
111
;
6.3.4.3 Edge enhancement
and vertical edges and lines are enhanced with
Edge enhancement in images is of unique importance
because the human visual system uses edges as a key
factor in the comprehension of the contents of an image
[2, 4, 5, 10, 13, 14]
. Edges in different orientations can
be selectively identified and enhanced. The edge-en-
hanced images may be combined with the original image
in order to preserve the context.
(
10
1
10
1
10
1
)
w
V
1
ðk; lÞ¼
or
(
101
101
101
)
w
V
2
ðk; lÞ¼
_