Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
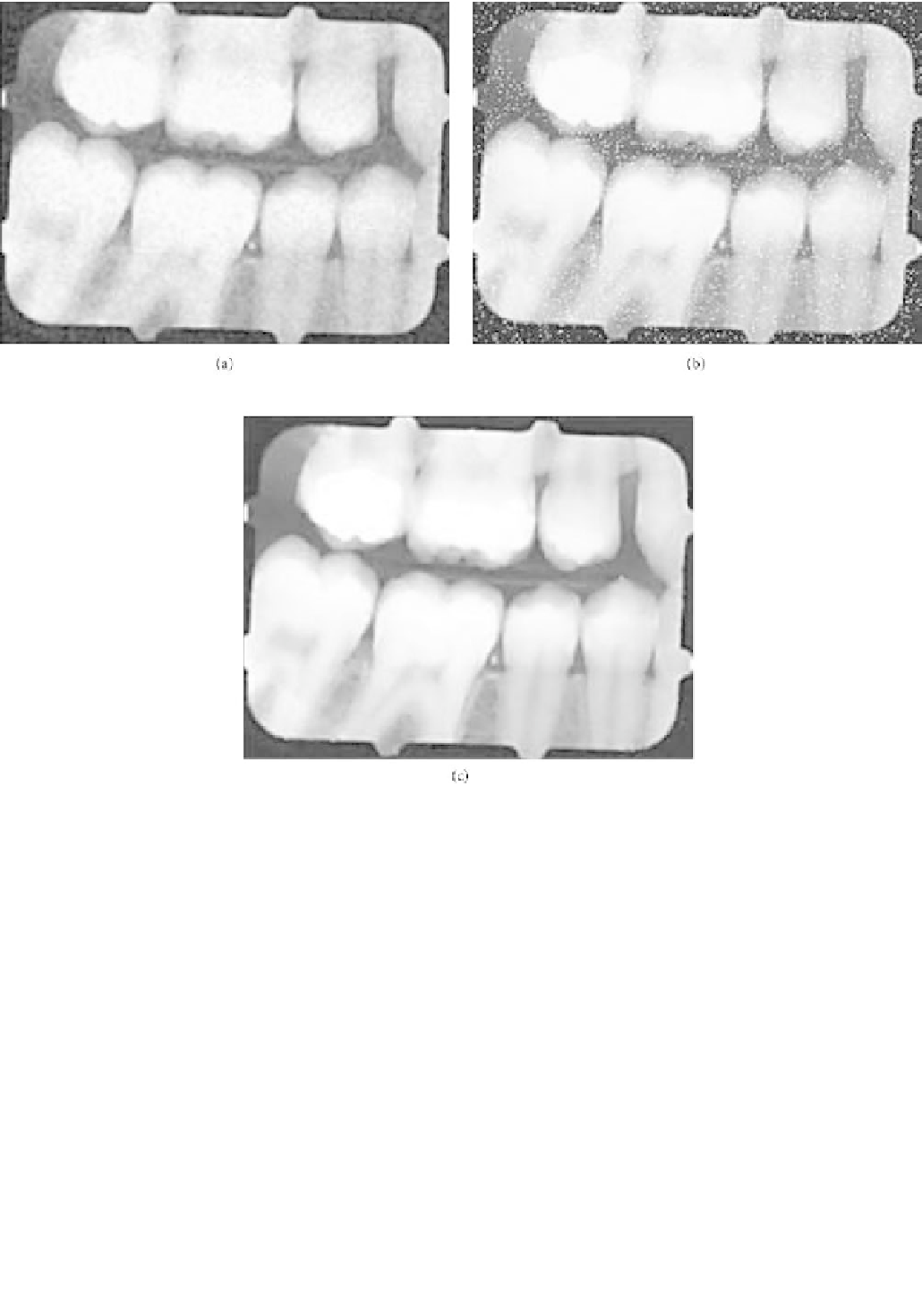
Figure 6.3-5 (a) Image in
Fig. 6.3-4b
enhanced with a 3 3 median filter. The median filter is not as effective in noise removal as
the mean filter of the same size; however, edges are not as severely degraded by the median filter. (b) Image in
Fig. 6.3-4a
with added
shot noise. (c) Image in
Figure 6.3-5
enhanced by a 3 3 median filter. The median filter is able to significantly enhance this image,
allowing almost all shot noise to be eliminated. This image has good diagnostic value.
The omnidirectional kernel (unsharp mask) enhances
edges in all directions:
hand, if we are interested in enhancing edges that are
consistent with the kernel and suppressing those that are
not, the output image may be added to the original input
image. This addition will most likely result in a non-
negative image.
Figure 6.3-6
illustrates enhancement after the appli-
cation of the kernels
w
H
1
,w
V
1
,
and
w
HP
to the image in
Figs. 6.3-3a
and
6.3-3g
.
Figures 6.3-6a-6.3-6c
show the
absolute value of the output images obtained with
w
H
1
,
w
V
1
, and
w
HP
, respectively, applied to the dental image
while
6.3-6d-6.3-6f
show the same for the brain
image. In
Fig. 6.3-7
, the outputs obtained with these
three kernals are added to the original
8
<
:
9
=
;
_
1
=
8
1
=
8
1
=
8
1
=
81
1
=
8
1
=
8
1
=
8
1
=
8
K
HP
ðk; lÞ¼
Note that the application of these kernels to a positive-
valued image can result in an output image with both
positive and negative values. An enhanced image with
only positive pixels can be obtained either by adding an
offset or by taking the absolute value of each pixel in the
output image. If we are interested in displaying edge-only
information, this may be a good approach. On the other
images of
Fig. 6.3-3a
and
6.3-3g
.
In this manner
the edge