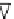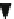Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
obstruction
Artery
FFP
Source/Detector
PET Film
Optical Fiber
PMMA
Water Layer
Figure 6.2-25 Angiology instrument using optical fibers.
diode used for sensor interrogation. The Fabry-P´rot
cavity of the fiber tip is formed by a polyethylene-tere-
phthalate film and the fiber end provides a fiber-polymer
acoustic impedance match. As the polymer film is in
contact with the tissue, the stress due to the thermo-
elastic wave modulates its thickness and, hence, the op-
tical phase difference between the interfering Fresnel
reflections from both sides of the film.
When the sensor head is coaxially positioned with
the delivery fiber, measurements are taken from the
center of the acoustic source, giving improved targeting
accuracy. This kind of photoacoustic spectroscopy has
been experimentally tested on postmortem human
aortas.
In addition to disturbing central circulation, cardio-
vascular diseases may influence the peripheral circulation
by affecting the microvascular perfusion in tissue. In-
sufficient peripheral circulation may produce chemical
gastric discomfort and ulcers. The best method for as-
sessment of microvascular perfusion is laser Doppler
flow monitoring in which the use of optical fibers can
improve the possibilities of both invasive and contact
measurements.
The basic concept of fiber-optic laser Doppler flow is
shown in
Figure 6.2-26
. Light from the He-Ne laser is
guided by an optical fiber to the tissue or vascular net-
work being studied. The light is diffusely scattered and
partially absorbed within the illuminated volume. Light
hitting a moving blood cell undergoes a small Doppler
shift due to the scattering particles.
Gastroenterology
The need for fiber optic systems to monitor
in vivo
the
functional aspect of the foregut is increasing. An impor-
tant parameter when studying the human foregut is the
gastric and esophageal pH. Monitoring gastric pH for long
periods serves to analyze the physiological pattern of
acidity. It provides information regarding changes in the
course of the peptic ulcer and enables assessment of the
effect of gastric antisecretory drugs. In the esophagus,
the gastroesophageal reflux, which causes a pH decrease
in the contents from 7 to 2, can determine esophagitis
with possible strictures and Barrett's esophagus, which is
considered a pheneoplastic lesion. In addition, in mea-
suring the bile-containing reflux, the bile and pH should
be measured simultaneously.
He-Ne Laser
Detector &
Processing
Tissue
Figure 6.2-26 The fiber-optic Doppler flow meter.