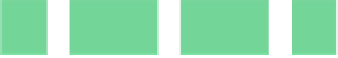Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
16
5
13
2
8107 1 4 6 9
19 3 10
16 4 14
9371112526715
13
14
19
9
1
15
6
17
4
15 17
16 18 13 3 14
11 16 12
172134526715
8910
61112
3
8
14 19 12
9
2
10
8
11
7
19 13
9
14
7
10
4
13 11
1
15
4
7
13 17 18 14
2
16 15
1
8
14
17
3
10
12
8
5
15
12
5
18 15
2
13 15
41816
19
3 6 8
6
11
c
d
21 6 23
16 11 24
14
4
18
13
51415
19225
165 8
14
1
3
6
23 18 17
12
17
17
18
2
10
10
3
15
9
7
13 16
2
14 15
6
16 10
5
12 22 14
1
19 15 13
2
1
3
4
5
2
8
8
8
17
7
12
6
10 14
7 4
11 13
451672589110112
3
22619
2113
7 1 5
24
14
8
25 13
5
9
21
4
13 16 17 14
2
9
6
12
12
2
18
10
2
9
3
1
8
11
1
4
6
21816
3
1 912
6
15
9
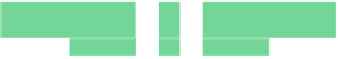
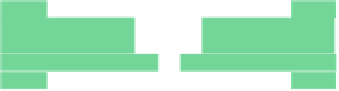
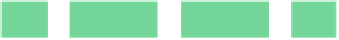
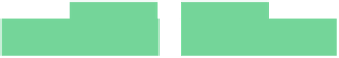
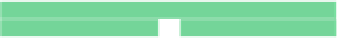
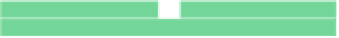
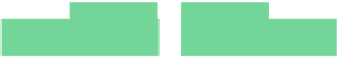
Fig. 6.18
Pin-assignment configurations for (
a
) multiplexed assay chip; (
b
)PCRchip;(
c
) protein
dilution chip; (
d
) multi-functional chip
6.7.2
Experimental Biochips
Next we apply the pin-assignment algorithm to the layouts of four laboratory proto-
types described in [
9
], namely a multiplexed assay biochip, a PCR biochip, a protein
dilution biochip, and a multifunction biochip. These layouts have subsequently been
incorporated in commercial chips [
20
]. Figure
6.18
shows their pin-assignment
configurations.
First we compare the number of pins and bioassay completion time between
the proposed general-purpose biochips and other biochips, which include the cross-
referencing biochip in [
6
], the bioassay-specific biochips in [
9
]and[
18
], and the
direct-addressing biochips. We implemented the ILP-based design method of [
18
]to
obtain a complete set of simulation results. Tables
6.3
and
6.4
present the simulation
results.
Note
that
both
the
cross-referencing
biochip
in
[
6
]
and
the
proposed
general-purpose biochip
are
bioassay-independent.
When
we
map
bioassays
to
bioassay-independent
chips,
droplet
operations
are
scheduled
after
the