Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
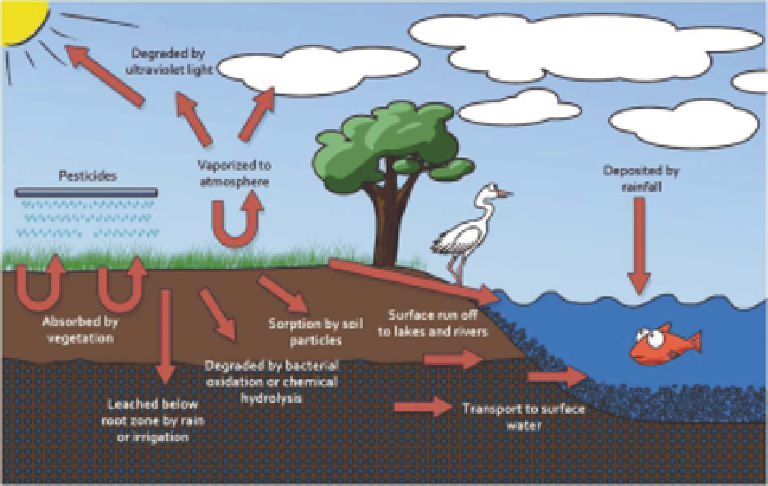
Figure 2.3
Transport, fate and behavior of pesticides.
The Environmental Working Group says that the benefits of eating fresh fruit and
vegetables outweighs the known risks of consuming pesticide residue, but the right
selection of fruit and vegetable is important, and should be based on individual deci-
sion. To make the proper decision, education of mainstream people and the availability
of information are essential preconditions.
In Europe, both Directive 91/414 on the placing on the market of PPPs and Regula-
tion 396/2005 on pesticide residues in food and feed aim at a high level of protection of
human health and the environment in EU, based on the toxicity and ecotoxicity of the
substances as well as their transport, fate and behavior in the environment (Figure 2.3).
5.3 Biocides
Biocides are chemical agents, defined by the European Biocidal Products Directive
(98/8/EC) as: “Active substances and preparations containing one or more active sub-
stances, put up in the form in which they are supplied to the user, intended to destroy,
deter, render harmless, prevent the action of, or otherwise exert a controlling effect on
any harmful organism by chemical or biological means.''
The European Commission adopted the original biocide proposal of 1998 in 1993.
The Directive 91/414/EEC on PPPs, adopted in 1991, served as a model for the new
Biocidal Product Directive (1998), which aims to harmonize the European market for
biocidal products and their active substances. At the same time it aims to provide a
high level of protection for humans, animals and the environment. The most popular
uses of biocides are summarized in Figure 2.4.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search