Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
[18]. Because the permeability of a hollow-fiber wall is similar to
that of vasculature, a hybrid artificial organ with hollow fibers that
hold cells, including a recombinant vector containing genes related
to cellular drug transport, has been developed. On the other hand,
creating an artificial liver is desired for treating various liver-related
diseases such as hemophilia and diabetes mellitus. However, the
fabrication of a functional artificial liver without cells is very difficult
because the liver plays an important role in regulating metabolism,
the detoxification of endogenous and exogenous substances, and
the production of hormones, which have very complex functions.
On the other hand, a hybrid artificial liver with hollow fibers whose
surfaces are coated with liver cells has been proposed [19-21].
Various hollow-fiber bioreactors have been developed, and these
technologies are expected to be applicable to the creation of 3D
cardiac tissue in the near future.
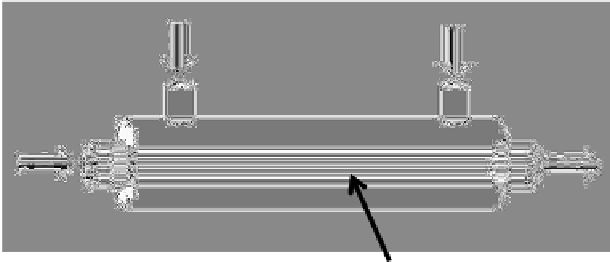
The outside flow of hollow fiber
The inside flow of hollow fiber
Hollow fiber
Figure 6e.2
Hollow-fiber bioreactor.
6e.4
Perfusion Bioreactor
Most of the cells are adhesion-dependent cells and are unable to
keep their viability without adhesion to solid or semisolid matter,
including dish and vessel surfaces. However, because a real in vivo
tissue consists of 3D clusters of cells, it is difficult to provide and
arrange a suitable habitat on a flat culture space such as a dish or
a flask. In a perfusion bioreactor, it is easy to arrange the shape of
a biodegradable scaffold for providing a suitable habitat for cells,