Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5 Isotherms Under Free Convection
At this stage of the experiments, the effects of the free convection are shown. It is
important to say that close to the heated cylinder the conduction dominates and the
resulting plumes get a concentrically circular shape, but if we turn away of the heated
cylinder, the convection begins to dominate the phenomenon and the plumes begin to
deform acquiring an ovoidal shape in its upper part. Figure
3
shows the evolution
of the plumes due the free convection. The time between successive images in the
sequence is 5min. Figure
4
shows the dependence of the dimensionless temperature
ʸ
Fig. 3
Sequence of infrared snapshots showing the evolution of the plumes under pure free con-
vection until a stationary state is reached. The time between consecutive snapshots is
t
=
5min
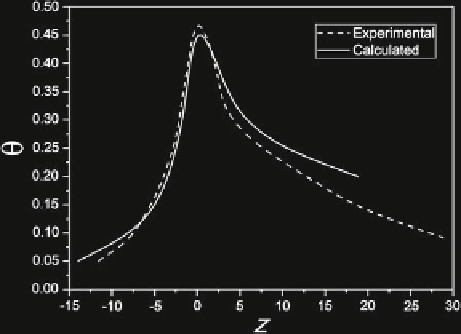
Fig. 4
Dependence of the numerically obtained dimensionless temperature
distribution (
continu-
ous line
) as a function of the dimensionless distance
z
(length takenwith reference to the
vertical
axis
passing through the heat source), as compared with distribution obtained experimentally (
dashed
line
) for the free convection case. The experimental
curve
was build up from the isotherms of
snapshot 6 in Fig.
3
ʸ

Search WWH ::

Custom Search