Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
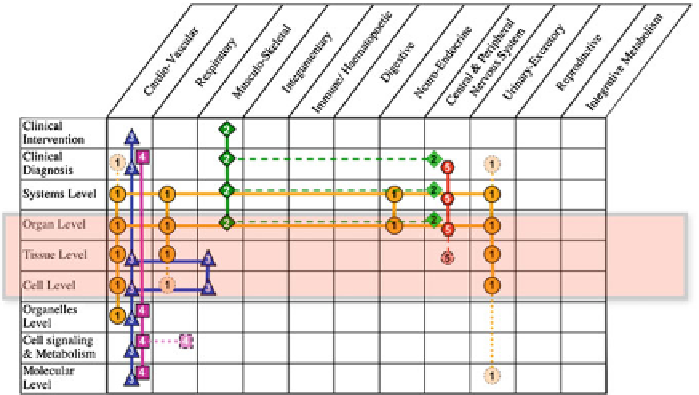
Fig. 2
Organ systems versus levels of organizations. Extracted from Thomas et al. (
2008
)
•
Complex physiological models: electrophysiological, material and coupling mod-
els of high complexity, with thousands of degrees of freedom per node.
•
Multi-physics problems: electrical activity, mechanical deformation and blood
flow.
In this paper we focus in the electro-mechanical problem.
2 Alya, an HPC-Based Computational Mechanics Tool
2.1 General Description
Alya is an HPC-based simulation tool for coupled multi-physics problems (see for
instance (Houzeaux et al. 2008, 2011). On general terms, it is a numerical solver for
coupled systems of partial differential equations (PDE), discretized on unstructured
meshes. It has a large database of element types, including low and higher order,
up to Q3. Transient problems are solved with either explicit or implicit schemes,
with time integration schemes of different order. Except for METIS (Metis
2015
)
and low level libraries (such asMPI), Alya has no dependency on third-party libraries,
being all solvers developed in-house. It is written in a modular way, with a kernel
that includes all the functionalities required to solve the physical problems including
parallelization and a set of modules, where each module represent a different PDE.
At the organ level, the cardiac computational model requires the solution of
the electrical component, which is a non-linear reaction-diffusion system; and the
mechanical component, which produces the deformation and a coupling model to
Search WWH ::

Custom Search