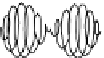Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
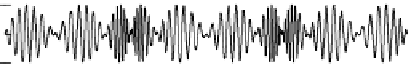
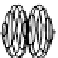
Figure 4.25
Complex signal
analysis of the amplitude and
frequency modulated time
series g(t). This time series was
calculated by sampling a
sinusoid h(t
n
) of period 1/1.47
cycles/kyr at intervals
t
n
= nΔt, with Δt = 4 years, and
n = 1, 2, …, 25,000, and
amplitude modulated by A(t
n
) =
sin[2πt
n
/(20 kyr)], such that
g(t
n
) = A(t
n
)·h(t
n
). For the
frequency modulation, the
timescale t
n
was replaced with
t'
n
= t
n
+ Δt[1 + sin(2πt
n
/40 kyr)],
to give g(t'
n
), which was then
resampled to a uniform rate of
Δt = 4 years as g(t). (a) The
modulated time series g(t);
(b) the complex signal G(t)
obtained using
hilbertsignal.m
(see Appendix), shown in 3D,
with the complex axis normal to
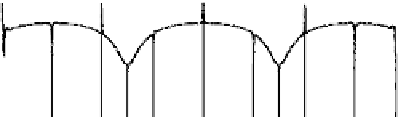
the page; (c) instantaneous
amplitude A(t); (d)
instantaneous phase θ(t); and
(e) instantaneous frequency f(t).
g(t)
(a)
1
0
-1
(b)
G(t)=g(t)+ig
*
(t)
1
0
-1
(c)
A(t) = IG(t)I
1
0
(d)
θ
(t)=arctan[g
*
(t)/g(t)]
10
0
-10
0
(e)
1
f(t) =d
θ
(t)/dt
2
0
20
40
60
Kiloyears
80
100
The input signal g(t) must have a zero mean and with a relatively narrow
band; most applications are preceded by band-pass filtering, for example,
filtering for the precession index, and analyzing the instantaneous amplitude
of the band-pass filtered signal to seek evidence for an orbital eccentricity
modulator (see Chapter 5).
This technique could be, but has not yet been, used to estimate accumulation
rate changes from stratigraphic sequences experiencing variable cycle
wavelengths. To whit, the example in Figure 4.25 was created to illustrate
Milankovitch influences on oxygen isotope Dansgaard-Oeschger cycles in the
GRIP (Greenland Icesheet Project) ice core; in particular, a strong 40 kyr (obliq-
uity) frequency modulation was found to affect the record, most probably due
to systematic error in the ice-flow based core chronology (Hinnov et al. 2002).
4.3.8
Coherency and Cross-Phase Analysis
Multivariate time series analysis is used to investigate two or more time series
that are hypothesized to have a relationship, e.g., cause and effect. Cross-
correlation analysis as a function of frequency is a fundamental tool for such