Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(
10.13
) can be in the unrealized form in
practice. There are many real situations when the realization of H
*
or N
*
system is
impossible. Some tasks and algorithms were described by Krapivin and Klimov
(1995, 1997).
The stochastic solution of Eqs. (
10.1
)
-
10.2.3 Study of the Simple Survivability Model
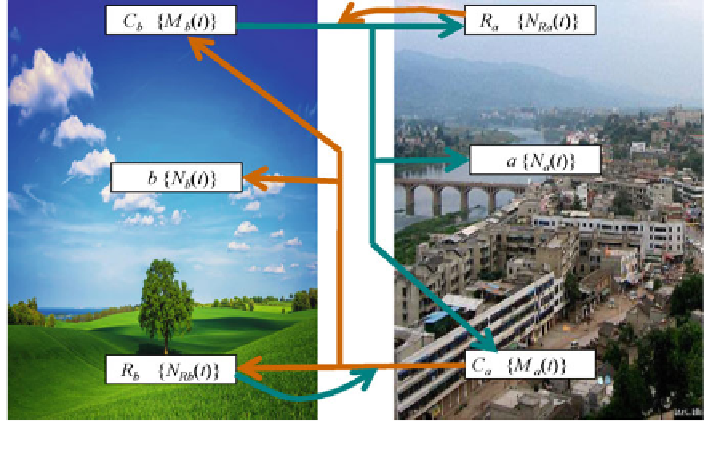
Let us consider the interaction of the two systems in the frame of diagram shown in
Fig.
10.1
. At the beginning, the systems H and N have, respectively, N
a
(0) and
N
b
(0) working elements, N
Ra
(0) and N
Rb
(0) protective elements, and M
a
(0) and
M
b
(0) active agents for undertaking action against an external medium. In this case,
we shall assume that the initial structures H
S
and N
S
of the systems are uniformly
filled with elements. This means that at the time t = 0 in any sphere with a
xed
radius
ʵ
, which is completely con
ned within system H, there are constant numbers
of elements.
Speci
c characteristics of all elements can be depending on the solved task. For
example, C
a
and C
b
element can be anthropogenic scenarios and diseases,
respectively. Feedbacks and medicine can be as R
b
and R
a
elements, respectively.
Elements a and b represent life conditions for people and hierarchy of ecological
systems, respectively. Certainly, detailed interpretation of all types of accomplished
elements depend on the spatial-temporal scale and knowledge base.
Fig. 10.1 Schematic diagram of the interaction of nature and humanity in the survivability
problem. Structure of system elements may be changed and added
Search WWH ::

Custom Search