Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
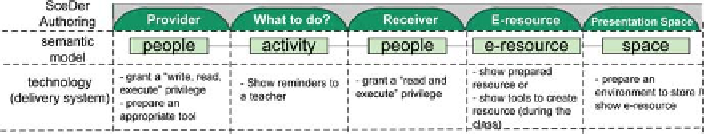
Fig. 22.6
A conceptual mapping between the semantic model and a distributed learning environ-
ment (Group Scribbles)
the last column,
presentation space
, the delivery system enables this environment
to be accessible by the people who are appeared in both the
provider
and
receiver
columns. It can be also interpreted that, for a certain
presentation space
, the system
grants a “write” privilege to the people in the
provider
column; provides an appro-
priate tool for them to create or show an e-resource, and grants a “read” privilege
for the people in the
receiver
column.
Results
We have carried out a pilot study with 18 master students in three classes to establish
proof of concept and to identify usability problems. After modifications to SceDer
based on the problems found in the pilot study, we carried out the main evaluation
with four classes of 20-30 students (aged 11-14) at a school where all students
routinely used tablet PCs in the classrooms.
The results have been analysed for three main aspects:
usability
,
usefulness
, and
expressiveness
. The first session had the aim of evaluating teaching and learning
with Group Scribbles alone by asking the two teachers to carry out lessons with-
out using SceDer. The second session was to evaluate the combined GS-SceDer by
asking the two teachers to design and conducts lessons and use GS-SceDer. Data
collection included video observations of the learning activities in the classroom
and interviews with teachers and students. The example scenarios designed by the
two teachers are as follows:
Charles designed a lesson for Year 7 students which aimed to teach them powers
of two (i.e. 2
2
,2
3
,2
4
,
) based on a game play. The format of the game was that
each group had to place answers in turn on chess board cells displayed as a back-
ground image. The answer in each cell had to be 2n + 1, where n starts with 1, on the
first cell. The teacher divided students into groups. The students who were sitting
around the same table were in the same group.
Dan designed a lesson to teach Year 9 students, which aimed to ask students'
opinions of a series of pictures. For example, Dan showed students a picture, a man
riding a big fish (see Fig. 22.5), and asked whether or not this photograph was gen-
uine and why. This lesson consisted of three pictures and the pictures were placed
as a background image on each board. The purpose of the lesson was to explore
...