Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
+V
DD
M
2
M
7
V
C2
M
8
V
B1
M
14
M
20
M
12
M
18
M
11
M
17
Y
M
1
M
4
X
Z+ Z-
M
10
M
15
M
16
M
9
M
6
V
C1
V
B2
M
5
M
3
M
19
M
13
−V
SS
Fig. 10.21
An exemplary realization of the balanced output third generation current conveyor
proposed by Sobhy and Soliman (Adapted from [
31
]
2009 Springer)
©
10.2.21 Balanced-Output Third Generation Inverting CC
Balanced output third generation inverting current conveyor was introduced by
Sobhy and Soliman in [
31
]. It combines the characteristic of an inverting current
conveyor and the third generation current conveyor and is characterized by the
following matrix equation.
0
1
0
1
0
1
I
Y
V
X
I
Zþ
I
Z
0
100
V
Y
I
X
V
Zþ
V
Z
@
A
¼
@
A
@
A
1000
0100
0
ð
10
:
22
Þ
100
A typical CMOS realization devised by the author of [
31
] is shown in Fig.
10.21
.
The applications, where balanced output third generation inverting current con-
veyor can be employed usefully, have been demonstrated in [
31
] and include the
realization of voltage-to-current converter, MOSFET-C lossless integrators and
biquad filters and MOSFET-C oscillators.
10.2.22 Voltage and Current Gain Second Generation
Current Conveyor (VCG-CCII)
The voltage and current gain CCII (VCG-CCII) was introduced by Marcellis
et al. in [
60
]. Its internal architecture can be understood by the schematic shown in
Fig.
10.22
. It is characterized by the following equations: I
y
¼
0V
x
¼
hV
y
,I
z
¼
kI
x



















































































































































































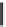

















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search