Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
+
+
+
+
+
+
-
-
+
-
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
-
-
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
-
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
-
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
-
Gd
-
+
Gd
-
Gd
Gd
Gd
Gd
+
+
-
+
-
+
+
+
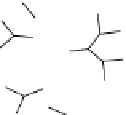
FIGuRe 8.4
polymers classified by increasing relaxivity. (a) The high flexibility of linear
polymers limits the relaxivity per gadolinium. (b) dendrimers are less flexible and exhibit
higher relaxivity but still undergo internal motion. (c) Relaxivity can be improved by intro-
ducing rigidification (with a cationic polymer and negatively charged Gd complexes in the
example earlier). (d) When the Gd complex is at the barycenter, it rotates at the rate of the
whole molecule, which leads to higher relaxivity.
charged pAMAM dendrimer was improved in the presence of a cationic poly(arginine),
introduced in order to induce internal rigidification by anionic/cationic interactions
(Fig. 8.4) [86]. The initial
r
1
value of 20.4 mM
−1
s
−1
of the free dendrimer reached
34 mM
−1
s
−1
in the presence of poly(arginine) (20MHz, 25°C). ultimately, higher
relaxivity could be obtained by placing the Gd
3+
complex at the barycenter of the
dendrimer as proposed by Fulton
et al
. [87]. In this system, the Gd
3+
chelate is at the
core and is connected to polyalcohol branches (Chart 8.5). This system results in a
Gd-OH
2
vector coupled more effectively to the rotational motion of the whole mole-
cule leading to improved relaxivity.
Interestingly, a new approach to introduce the Gd
3+
into the dendrimer developed
by nwe
et al
. was shown to influence highly the relaxivity. While the Gd
3+
is classi-
cally introduced in the last step of the synthesis into the chelating agent already
conjugated to the dendrimer, the novelty was to conjugate the preformed Gd
3+
-ligand
complex to the dendrimer [88]. This method leads to a better control of the free
dTpA/complexed dTpA ratio with virtually 0% of free ligand on the final dendrimer
with the preligation method, while approximately 20% of ligands remain unoccupied
with the classical method. The relaxivity per Gd increased from 13.9 mM
−1
s
−1
for the
postligation method to 26.9 mM
−1
s
−1
(at 3 T and 22°C) with this new method. It was
hypothesized by the authors that carboxylates from the free unoccupied dTpA moi-
eties in the vicinity of the Gd
3+
complex were responsible for disturbing the water
exchange when dendrimers are formed by the classical method, which is not the case
with the preligation method.
8.3.2.2 Dendrimers Biodistribution and Applications in MRI
Passive Distribution
The biodistribution of dendrimers and their potential appli-
cations in MRI are primarily governed by their size as observed in many studies
with pAMAM dendrimers (Fig. 8.5). They exhibit prolonged circulation time as
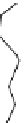









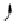


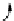

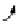


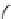
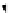

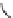




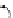














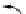

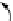

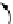


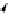


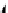
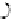
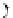

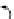

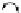










































Search WWH ::

Custom Search