Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
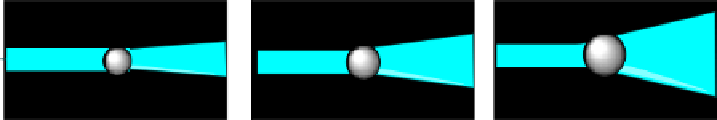
figure 6.26
Principle of measuring size of a nanoparticle with flow cytometry. Smaller
particles produce less front scattering.
most common configuration)—are recorded. The magnitude of the forward scatter is
to the first approximation proportional to the size of the particle. Small particles will
produce small forward scattering, while large particles produce larger scattering
(fig. 6.26). Particles as small as 58 nm can be detected, allowing to distinguish the
differences in the size distributions between nanoparticles even if the difference in
diameter was only 25 nm [107]. flow cytometry has thus been utilized for the
characterization of gold nanorods, viral nanoparticles [108], and quantum dots.
refereNces
[1] McCarthy DW, Shefer RE, Klinkowstein RE, Bass la, Margeneau WH, Cutler CS,
anderson CJ, Welch MJ. Efficient production of high specific activity 64Cu using a bio-
medical cyclotron. Nucl Med Biol 1997;
24
:35-43.
[2] Zeng D, anderson CJ. Rapid and sensitive lC-MS approach to quantify non-radioactive
transition metal impurities in metal radionuclides. Chem Commun (Camb) 2013;
49
:
2697-2699.
[3] Shokeen M, fettig NM, Rossin R. Synthesis, in vitro and
in vivo
evaluation of radiola-
beled nanoparticles. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;
52
:267-277.
[4] Hendee WR, Morgan CJ. Magnetic resonance imaging. Part I—physical principles. West
J Med 1984;
141
:491-500.
[5] Chandra T, Pukenas B, Mohan S, Melhem E. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance
angiography. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N am 2012;
20
:687-698.
[6] ferre JC, Shiroishi MS, law M. advanced techniques using contrast media in neuroim-
aging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N am 2012;
20
:699-713.
[7] Jackson a, o'Connor JP, Parker gJ, Jayson gC. Imaging tumor vascular heterogeneity
and angiogenesis using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Clin
Cancer Res 2007;
13
:3449-3459.
[8] Hao D, ai T, goerner f, Hu X, Runge VM, Tweedle M. MRI contrast agents: basic chem-
istry and safety. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012;
36
:1060-1071.
[9] Cromer Berman SM, Walczak P, Bulte JW. Tracking stem cells using magnetic nanopar-
ticles. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 2011;
3
:343-355.
[10] Kanwar RK, Chaudhary R, Tsuzuki T, Kanwar JR. Emerging engineered magnetic
nanoparticulate probes for targeted MRI of atherosclerotic plaque macrophages.
Nanomedicine (lond) 2012;
7
:735-749.
[11] lee N, Hyeon T. Designed synthesis of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for effi-
cient magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chem Soc Rev 2012;
41
:2575-2589.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search