Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
With cages
Blood only
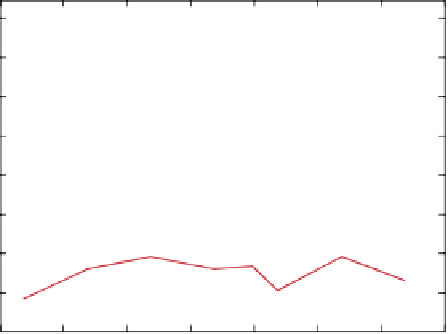
760
770
780
790
Laser wavelength (nm)
800
810
820
830
(b)
(c)
2 mm
2 mm
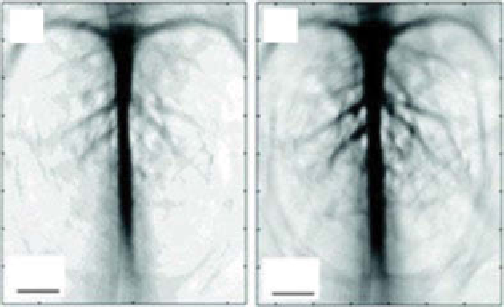
figure 5.15
(a) The measured OA signal amplitude generated with and without gold
nanocages in rat blood at several wavelengths. Noninvasive OA imaging of a rat's cerebral
cortex (b) prior to the injection of nanocages and (c) 2 h after the final injection, which is the
peak enhancement point. (Reproduced with permission from Ref. [151]. © American chemical
society.)
rat's cerebral cortex after the injection of gold nanocages. The images clearly
demonstrate that the rat brain vasculature could be visualized with great clarity and
enhanced contrast.
As shown in figure 5.16, the sLN, located quite deep below the skin's surface,
could be imaged with OA technology using gold nanocages. After the injection, PA
signals increased with time, which indicated gradual accumulations of the nanocages
in the tissue of interest (sLN).
One of the advantages of using gold nanocages for applications in biomedical imaging
lies in the well-established surface chemistry of Au, including functionalization with
a variety of targeting moieties to further enhance the contrast of the targeted region.
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search