Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
10 ms
Encapsulated
pyranine
SO
3
Na
NaO
3
S
SO
3
Na
O
-
NaOH
SO
3
Na
l
450
NaO
3
S
SO
3
Na
O
-
SO
3
Na
NaO
3
S
SO
3
Na
NaOH
Free
pyranine
OH
SO
3
Na
NaO
3
S
SO
3
Na
OH
t
(ms)
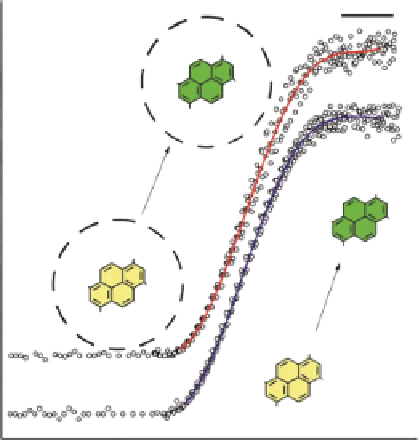
Figure 4.10
Change of fluorescence intensity as function of time in stopped flow experi-
ments with free and NC-encapsulated dyes. Response of free pyranine (bottom curve) and
pyranine entrapped within NCs (top curve) to NaOH. (Adapted with permission from Ref.
[56]. © Royal Society of Chemistry.)
of molecules into hollow NCs is based on reversible coentrapment of components
that form a noncovalent complex (Fig. 4.11b) [34, 57, 58]. Here, components can
enter the capsule individually through the nanopores. The complex is too big to pass
through the pores, and it remains entrapped [59, 60]. The dissociation of the complex
upon external stimulus triggers the release of individual components. In one imple-
mentation [58], we used a conformationally flexible crown compound. It is likely
that this concept will be applicable to other systems, where the minimal cross section
of the complex is bigger than the effective minimal cross sections of individual com-
ponents. One can envision further extension of this concept into metal-mediated
release of biologically active molecules or into noncovalent assembly of functional
devices, such as nanoreactors or nanosensors. This approach may be further extended
to other materials with uniform nanopores.
Several examples of stimuli-responsive encapsulation of low- or high-molecular-
weight species were reported for LBL microcapsules (Fig. 4.11c). For example, a
pH change can induce electrostatic repulsion between the two types of polyelectro-
lyte, while osmotic pressure can build up when ions diffuse to the interior of the
vesicles to compensate the charges. The resulting forces form holes in the polyion
shells. under standard aqueous conditions, the capsule shell is permeable to low-
molecular-weight compounds such as ions and small drug molecules but imperme-
able to macromolecular components (
M
w
> 5 kDa) [61]. The loading of larger species
Search WWH ::

Custom Search