Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
Hydrophilic
block
a
b
c
2D Oligomeric patch
Self assembly
in water
Hydrophobic
block
Loosely cross-linked
polymer nanocapsules
Extensively cross-linked
polymer nanocapsules
containing disulfide loops
f
e
d
200 nm
100 nm
100 nm
5nm
50nm
1μm
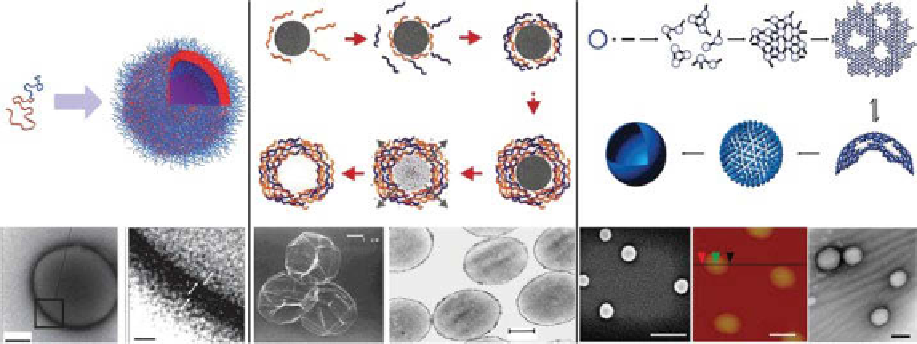
Figure 4.7
(A) Schematic of a polymersome formation and positive staining electron micrographs showing the
membrane conformation of PEO50-PBO70 polymersomes. (B) Schematic illustration of the polyelectrolyte deposition
process and of subsequent core decomposition and SEm and TEm images of polyelectrolyte shells. The initial steps
(a-d) involve stepwise film formation by repeated exposure of the colloids to polyelectrolytes of alternating charge. The
excess polyelectrolyte is removed by cycles of centrifugation and washing before the next layer is deposited. After the
desired number of polyelectrolyte layers is deposited, the coated particles are exposed to 100 mm HCl (e). The core
immediately decomposes, as evidenced by the fact that the initially turbid solution becomes essentially transparent within
a few seconds. Three additional washings with 100 mm HCl ensure removal of the dissolved melamine formaldehyde
(mF) oligomers. Finally, a suspension of free polyelectrolyte hollow shells is obtained (f). (Reprinted with permission
from Ref. [32]. © Wiley.) (C) Proposed mechanism of the self-assembled polymer NC formation and SEm, AFm, and
HRTEm images of polymer NCs. (Reprinted and adapted with permission from Ref. [40]. © American Chemical
Society.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search